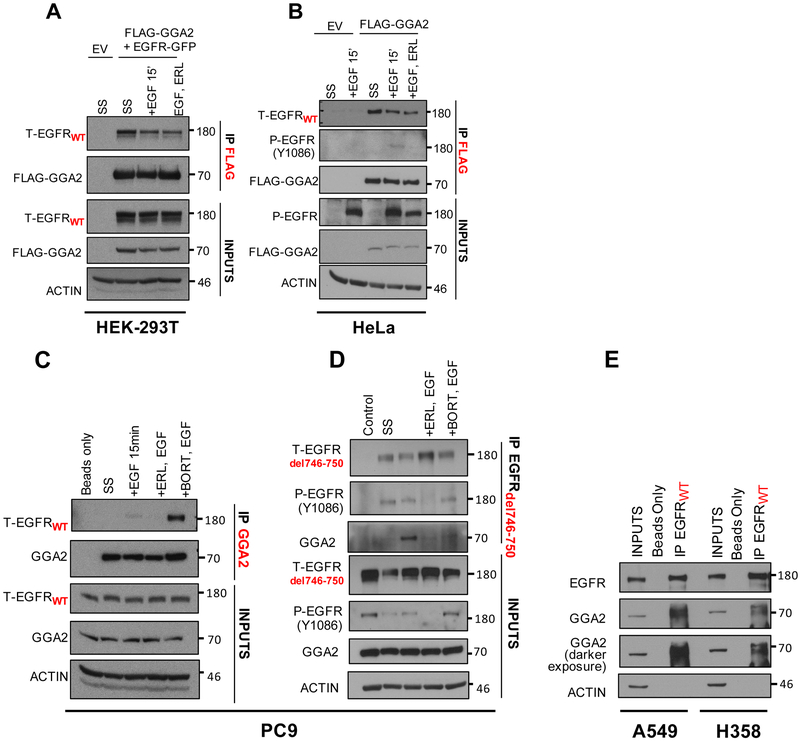
Figure 4. EGFR and GGA2 physically interact in lung adenocarcinomas.
(A) HEK-293T cells were transfected with empty vector (EV) or FLAG-GGA2 and EGFR-GFP and (B) HeLa cells were transfected with empty vector (EV) or FLAG-GGA2. 48 hours later, cells were cultured 3 different conditions: SS: serum starvation for 2 hours, +EGF: serum starvation followed by stimulation with EGF ligand for 15 mins, +ERL,EGF: serum starvation followed by incubation with Erlotinib and subsequent stimulation with EGF ligand for 15 mins. FLAG-GGA2 was pulled down with anti-FLAG beads and probed for interaction with EGFR by Western Blot analysis. In HEK-293T cells (A), overexpressed GGA2 interacted with overexpressed EGFR in all 3 conditions. In Hela cells (B), overexpressed GGA2 interacted with endogenous EGFR in all 3 conditions. (C, D) PC9 cells were cultured 4 different conditions: SS: serum starvation for 2 hours, +EGF (50ng/ml): serum starvation followed by stimulation with EGF ligand for 15 mins, +ERL,EGF: serum starvation followed by incubation with Erlotinib (1uM) and subsequent stimulation with EGF ligand for 15 mins, +BORT,EGF: serum starvation followed by incubation with Bortezomib (2uM) and subsequent stimulation with EGF ligand for 15 mins. We performed IP’s with anti-GGA2 antibody (C) and reverse IP’s with anti-EGFRdel746-750 antibody (D). In PC9 cells, GGA2 interacted with both EGFRWT (C) and EGFRdel746-750 (D) especially after receptor stimulation with EGF ligand and upon inhibiting proteasomal degradation with Bortezomib. (E) When probed for interaction in A549 and H358 cell lines by IP GGA2/WB EGFRWT, endogenous GGA2 interacted with EGFRWT in both cell lines.