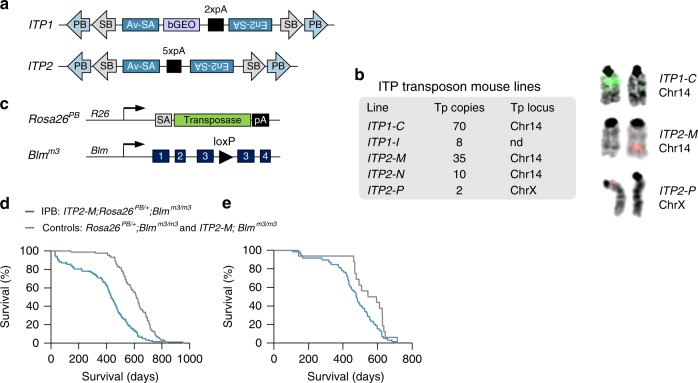
Fig. 1.
A PiggyBac transposon system for recessive screening in mice. a Structure of "inactivating transposons" ITP1 and ITP2. b Transgenic mouse lines generated using ITP1 or ITP2. Transposon copy numbers within the transgene array as well as the chromosomal donor locus of the array are shown. Chromosomal donor loci for different lines are shown on the right, as detected by fluorescence in situ hybridization with transposon-specific probes. Note that the ITP2-M and ITP2-N mouse lines emerged from a single founder animal. c Structures of the Rosa26PB and Blmm3 alleles as described earlier20,33. The Rosa26PB knock-in allele expresses the insect version of the PiggyBac transposase constitutively driven by the endogenous Rosa26 promoter. d, e Kaplan–Meier plots showing survival of IPB and control mice. In d the whole cohort is shown (n = 123 [IPB], n = 87 [controls]; p < 0.0001, log-rank test). e represents survival curves for mice displaying hematopoietic tumors characterized histopathologically (n = 59 [IPB], n = 16 [controls]; p = 0.025, log-rank test). PB PiggyBac, SB Sleeping Beauty, Av-SA adenovirus-derived splice acceptor, bGEO β-galactosidase/neomycin resistance reporter including the bovine growth hormone polyadenylation signal, En2-SA Engrailed-2 exon-2 splice acceptor, pA SV40 bidirectional polyadenylation signal, Tp transposon, R26 Rosa26, SA splice acceptor, Blm Bloom syndrome RecQ like helicase, nd not done