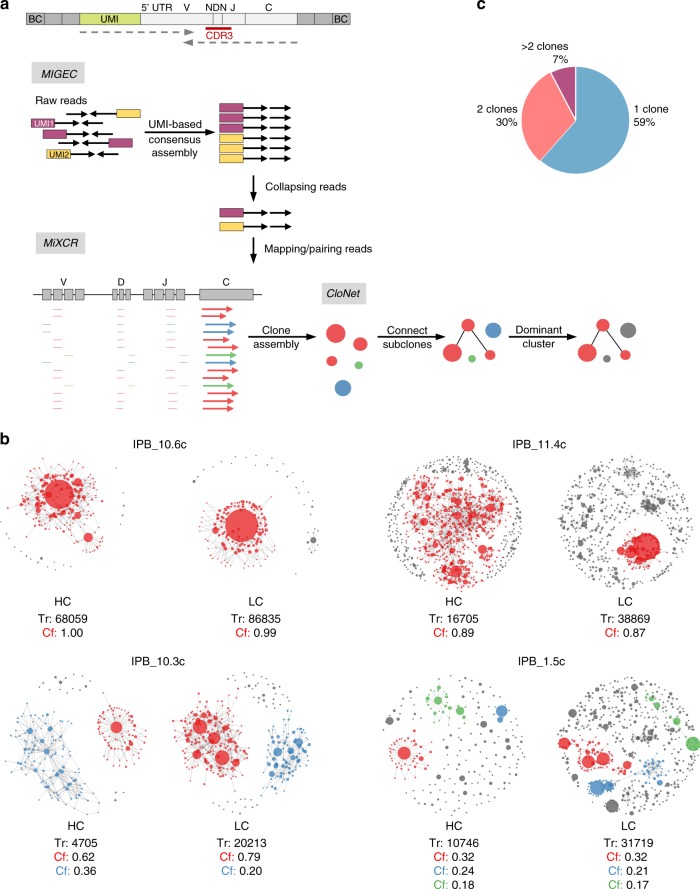
Fig. 3.
Clonality analysis of DLBCLs by immune repertoire sequencing. a Workflow for B-cell receptor repertoire analysis. Full-length amplification and sequencing of immunoglobulin heavy and light chain variable regions was performed from bulk tumor tissue (n = 30) of ITP2-M;Rosa26PB/+;Blmm3/m3 (IPB) mice. Top image shows exemplary cDNA product after library preparation with amplified variable and constant region of the immunoglobulin heavy chain (light gray). Unique molecular identifiers (UMI; green) and adapters and barcodes for sequencing (dark gray) were introduced during library preparation. Dotted arrows indicate reads for 300 bp paired-end sequencing. Sequenced raw reads were de-multiplexed and a consensus read sequence for each UMI was assembled with MIGEC. All reads containing an identical UMI were collapsed into one read. MiXCR was used for mapping of reads to mouse reference sequences and clonotype assembly based on the complementarity-determining region 3 (CDR3) region. To visualize the clonal structure of individual tumors, we developed CloNet, a pipeline for generation of clonality network plots. b Exemplary clonality network plots derived from four different mouse DLBCL samples. Plots display clonal structures of immunoglobulin heavy and light chains. Each clone (defined by a unique CDR3 sequence) constitutes a node of the clonality network. The size of the node scales with the third root of the count of the reads assigned to it. A link between two nodes was drawn if the clones mapped to identical V and J genes and differed by at most 1 bp in their CDR3 sequence. The complexity of the branching of a clone (i.e. number of subclones) is a measure for the grade of somatic hypermutation. Clones defined by a unique V(D)J rearrangement that contained more than 10% of the total reads are highlighted in color. Two monoclonal (IPB_10.6c and IPB_11.4c) samples, one biclonal (IPB_10.3c) and one oligoclonal (IPB_1.5c) sample are shown. c Proportion of monoclonal (1 clone), biclonal (2 clones), and oligo-/polyclonal (>2 clones) DLBCL samples. BC barcode, V variable gene segment, NDN diversity gene segment, J joining gene segment, C constant gene segment, HC heavy chain, LC light chain, Tr total reads, Cf fraction of clone