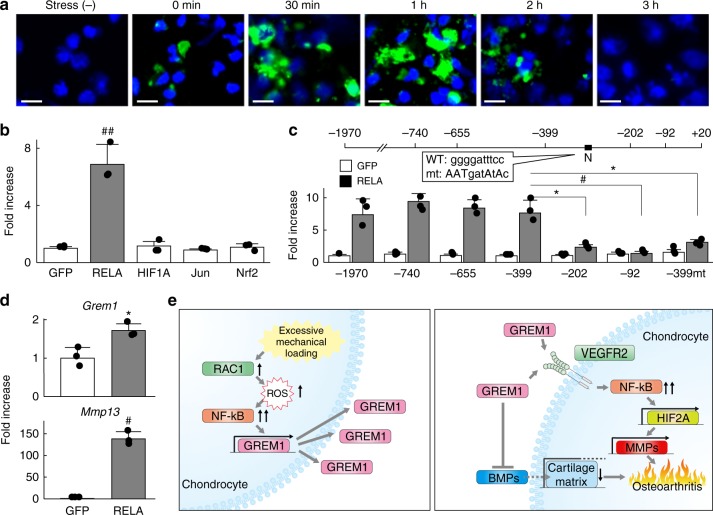
Fig. 8.
The ROS- NF-κB pathway enhances transcriptional induction of gremlin-1. a Fluorescence imaging time-course of ROS production in mouse primary chondrocytes after cyclic tensile strain loading. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bars, 20 µm. b Luciferase assay using ATDC5 cells co-transfected with human GREM1 promoter (from −1970 to +20 bp relative to the transcriptional start site) and each expression vector. ##P < 0.001 versus GFP (one-way ANOVA test). c 5ʹ-deletion and mutation analyses of the luciferase assay. N: NF-κB motif, −399mt: reporter construct from −399 to +20 bp in which NF-κB motif is mutated. *P < 0.05, #P < 0.005 (Student’s unpaired two-tailed t-test). d mRNA levels of Gremlin-1 and Mmp13 in mouse primary chondrocytes transfected with RelA or GFP. *P < 0.05, #P < 0.005 versus GFP (Student’s unpaired two-tailed t-test). e Schematic diagram representing molecular pathways in which excessive mechanical loading induces osteoarthritis development through gremlin-1. All data are expressed as mean ± SD of biologically independent three samples per group