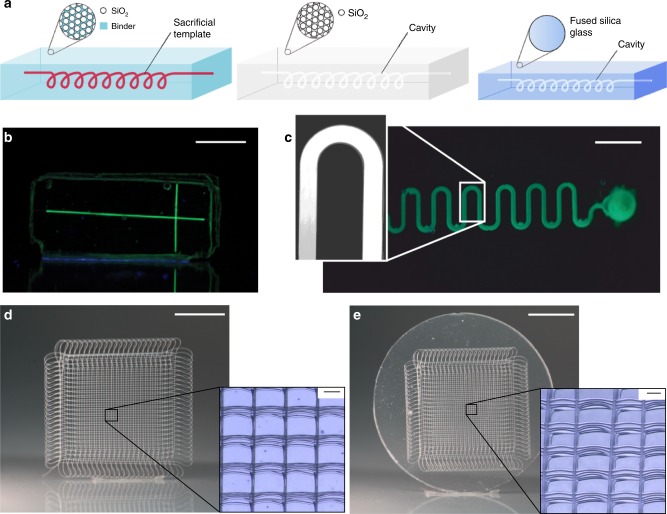
Fig. 1.
Fabrication of suspended hollow microstructures in fused silica glass. a Polymeric filaments are embedded in an amorphous silica nanocomposite. The polymerized nanocomposite is turned into fused silica glass via thermal debinding and sintering. The polymeric template is removed during the thermal debinding process and leaves the according hollow cavity. b Microfluidic fused silica chip fabricated by embedding a nylon thread (scale bar: 9 mm). c Microfluidic meander fabricated by embedding polymerized PEGDA structured by microlithography (scale bar: 11 mm). d A mesh structure made from poly(ε-caprolactone) using melt electrowriting (scale bar: 5 mm). The inset shows the microscopy image of the mesh with a fiber diameter of 25.0 µm (scale bar: 100 µm). e Inverse hollow mesh structure in fused silica glass (scale bar: 4.5 mm). Inset shows the microcavities with a width of around 18.4 µm (scale bar: 100 µm)