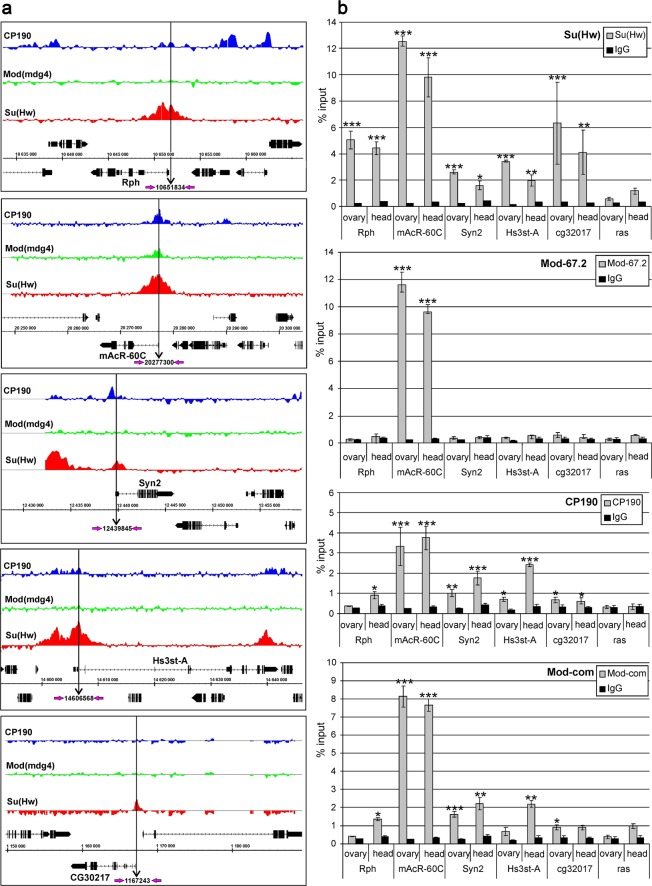
Figure 1.
Model system for studying Su(Hw)-dependent repression. (a) Genome browser view of insulator protein binding. The regions used in qPCR are indicated by vertical black arrows and numbered according to their chromosome position (FlyBase, 2006). The names of identified genomic regions are given next to the schemes of model genes. (b) ChIP-qPCR data on the binding of insulator proteins to the promoters in the ovaries and heads of females. ChIP was performed with antibodies against Su(Hw), Mod(mdg4)-67.2 (Mod-67.2, the C-terminal region corresponding to the specific isoform), CP190, Mod-com (the region common to all Mod(mdg4) isoforms), and nonspecific immunoglobulins (IgG, control). The ras64B coding region (ras) was used as a control devoid of Su(Hw) binding sites. The percent recovery of immunoprecipitated DNA (Y axis) was calculated relative to the amount of input DNA. Error bars indicate standard deviation of three independent biological replicates. Statistical analysis (Student’s t-test) was performed relative to protein binding to the ras64B coding region. Asterisks indicate significance levels of *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, or ***p < 0.001 (here and in Figs 2–5).