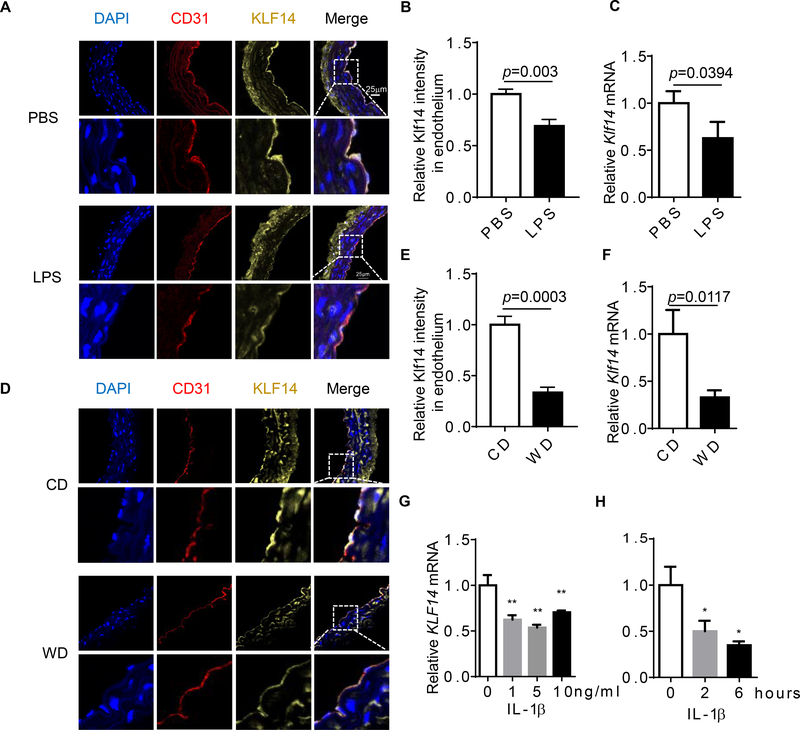
Fig. 1. Endothelial KLF14 is down-regulated in both acute and chronic inflammatory conditions.
(A-C) Eight-week-old male C57BL/6J mice were treated with PBS or lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 20 mg/kg) via intraperitoneal injection. Six hours later, aortas were collected. (D-F) Six-week-old C57BL/6J mice were fed chow diet (CD) or western diet (WD) for three months. Aortas were collected. Adventitia was carefully removed from aortas in both conditions before tissue mRNA was extracted. Expression of KLF14 was determined by immunofluorescence and confocal images (A and D) and qRT-PCR (C and F). (G) Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were stimulated with the indicated concentration of interleukin 1β (IL-1β) for 6 hours and Klf14 levels were detected by qRT-PCR. (H) IL-1β (10ng/ml) was used to stimulate HUVECs in a time course experiment and KLF14 levels were detected by qRT-PCR. (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01, compared to PBS, CD, or no treatment group.)