Figure 1.
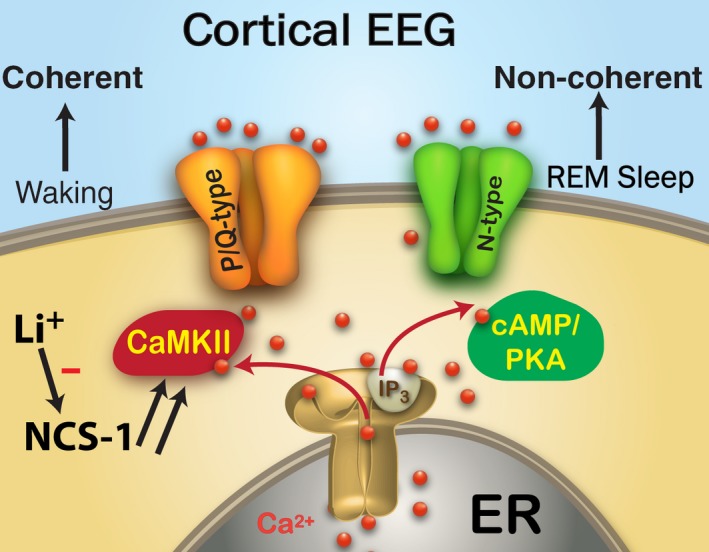
Waking vs REM sleep gamma mechanisms. The Cortical EEG looks the same during waking and REM sleep, but it is coherent across regions during waking and non‐coherent during REM sleep. The cortical EEG, therefore, is driven by the RAS, which regulates waking and sleep. Cells in the PPN modulate gamma oscillations during waking through P/Q‐type calcium channels that are under the control of CaMKII, while cells in the PPN that modulate REM sleep do so through N‐type calcium channels that are under the control of cAMP/PKA. In BD, NCS‐1 is over expressed (note double arrows to denote over expression) and its excess decreases CaMKII and P/Q‐type driven gamma oscillations to decrease the maintenance of gamma band activity during waking. This may also lead to excessive REM sleep drive. Li+ inhibits the action of over expressed NCS‐1 in order to restore the generation of gamma band oscillations during waking [Colour figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
