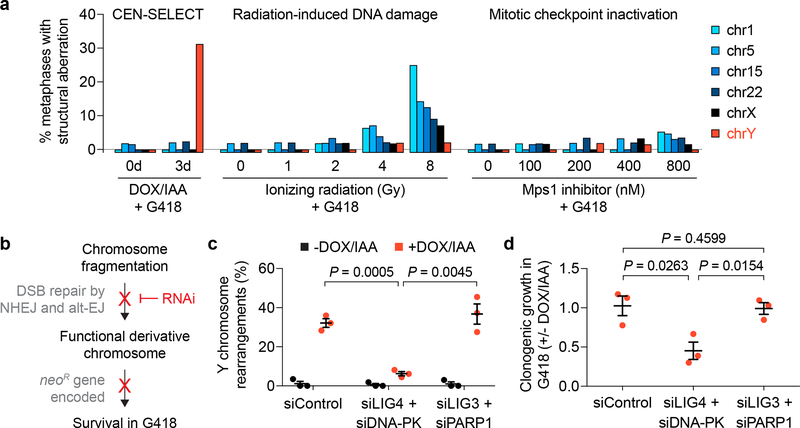
Figure 4 |. Chromosome rearrangements develop with high frequency and specificity through classical non-homologous end joining repair.
a) DLD-1 cells carrying a CENP-AC–H3 rescue gene were treated as indicated in Supplementary Fig. 7e, followed by metaphase spread preparation and hybridization to the indicated chromosome paint probes. Metaphases were examined for structural rearrangements affecting each chromosome. Bar graph represents n = 42–65 metaphases scored per chromosome per condition, analysing a total of 1,968 metaphase spreads (exact sample sizes provided in Supplementary Fig. 7g). b) Schematic of experimental hypothesis tested in panels c and d. NHEJ, non-homologous end joining; alt-EJ, alternative end joining. c-d) DLD-1 CENP-AC–H3 rescue cells were treated with or without 3d DOX/IAA and transfected with the indicated siRNAs simultaneous with DOX/IAA washout for an additional 3d. Cells were then re-plated into G418 medium for c) 10d selection followed by metaphase FISH using MSY/YqH probes (102–159 metaphase spreads per condition) or d) 14d at single-cell density for colony formation assays. Data in c and d represent the mean ± SEM of n = 3 independent experiments; P-values were derived from two-tailed Student’s t-test comparing groups as indicated.