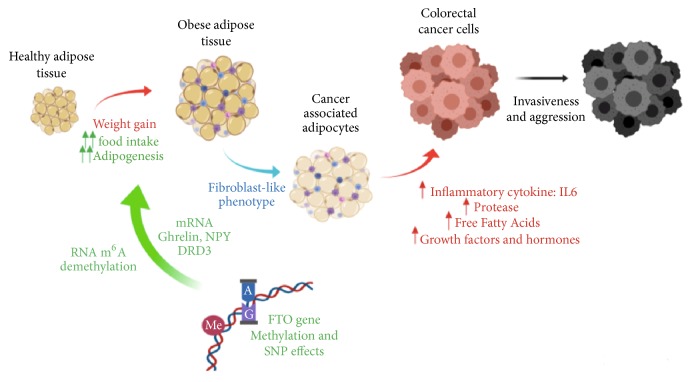
Figure 1.
Proposed mechanisms linking FTO gene, obesity, and cancer. The weight gain, malfunctioning of the FTO gene leading to increase food intake and adipogenesis process could develop obesity, especially abdominal obesity. It is also linked to adipocyte hypertrophy and hypoxia. The hypertrophied adipose tissue acquires endocrine characteristics like fibroblasts, which produce an increase of adipokine and hormone secretion profile, proteases, and free fatty acids that may promote the stimulation of a microenvironment favorable for not only tumorigenesis, but acquire new properties as invasiveness and aggression. Abbreviations: m6A: N6-Methyladenosine; NPY: Neuropeptide Y; DRD3: Dopamine Receptor type D3; FTO: Fat-mass and obesity-associated; SNP: Single-nucleotide polymorphism; IL6: Interleukin 6.