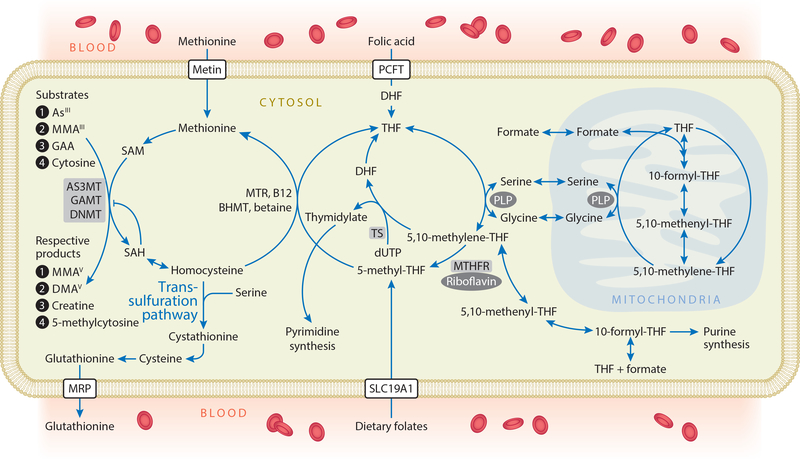
Figure 4.
One-carbon metabolism. FA, arising from fortified foods or nutritional supplements, is reduced to DHF and THF by dihydrofolate reductase. Serine hydroxymethyl-transferase transfers one-carbon units from serine to THF, with PLP as a coenzyme, forming 5,10-methylene-THF. This is either used for the synthesis of thymidylate or reduced to 5-methyl-THF. Dietary folates can enter one-carbon metabolism as 5-methyl-THF. The methyl group of 5-methyl-THF is transferred to homocysteine in a reaction catalyzed by MTR and utilizing B12 as a cofactor, generating methionine and THF. Alternatively, in the liver, betaine can donate a methyl group for the remethylation of homocysteine in a reaction catalyzed by BHMT. Methionine adenosyltransferase enzymes activate methionine to form SAM—the methyl donor for numerous acceptors, including arsenicals, GAA (the precursor to creatine), and DNA—in reactions that involve substrate-specific methyltransferase enzymes. These methylation reactions generate the methylated products and SAH, a potent product inhibitor of most methyltransferases. SAH is hydrolyzed to generate homocysteine, which is either remethylated to regenerate methionine or directed to the transsulfuration pathway and ultimately glutathionine synthesis. Abbreviations: AS3MT, arsenic-3-methyltransferase; BHMT, betaine homocysteine methyltransferase; DHF, dihydrofolate; DMAsV, dimethylarsinic acid; DNMT, DNA methyltransferases; FA, folic acid; GAA, guanidinoacetate; GAMT, guanidinoacetate-N-methyltransferase; InAsIII, arsenite; MMAsIII, monomethylarsonous acid; MMAsV, monomethylarsonic acid; MRP, multidrug resistance proteins; MTR, methionine synthase; PCFT, proton coupled folate transporter; PLP, pyridoxal phosphate; SAH, S-adenosylhomocysteine; SAM, S-adenosylmethionine; SLC19A1, solute carrier family 19 (folate transporter), member 1, also known as RFC1; THF, tetrahydrofolate; TS, thymidylate synthetase.