Fig. 2. Chemical synthesis of Bcr/Abl proteins via native chemical ligation.
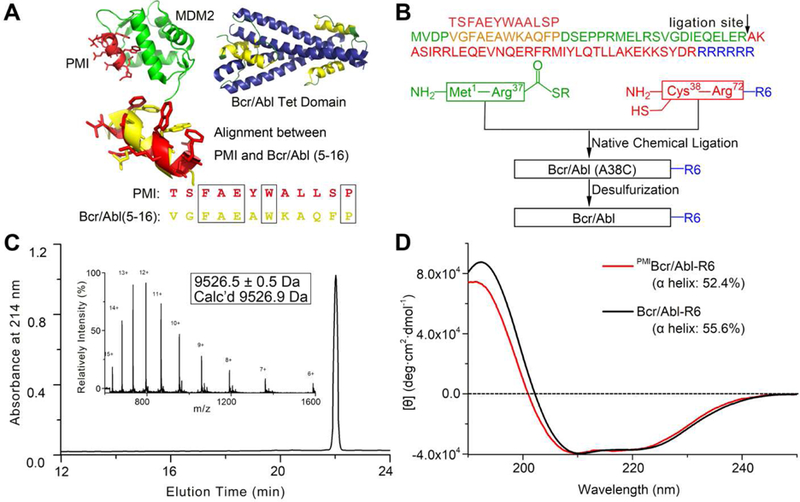
(A) Structure-based rational design of PMIBcr/Abl-R6. The crystal structures of PMI (red) in complex with MDM2 (green) [39] and of the tetramerization domain of Bcr/Abl (blue/yellow) [34] are shown in ribbons. The dodecameric peptide PMI (TSFAEYWALLSP) and residues 5–16 of Bcr/Abl (VGFAEAWKAQFP) share certain degrees of sequence and structural similarity. (B) Total chemical synthesis of PMIBcr/Abl, Bcr/Abl-R6 and PMIBcr/Abl-R6 via native chemical ligation [40, 41]. All peptides were synthesized on appropriate resin using Boc-chemistry solid phase peptide synthesis [66]. Ligation reactions were carried out in 0.1 M phosphate buffer containing 6 M GuHCl, 100 mM MPAA and 40 mM TCEP, pH 7.4. Desulfurization of the ligation product was achieved by dissolving the peptide at 1 mg/mL in 0.1 M phosphate buffer containing 6 M GuHCl, 0.01 M VA-044, 0.5 M TCEP, 20% t-BuSH. (C) PMIBcr/Abl-R6 analyzed by HPLC and electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS). Analytical HPLC was performed on a reversed-phase C18 column (Waters XBridge™ 3.5 µm, 4.6×150 mm) at 40 °C. (D) Circular dichroism (CD) spectra of Bcr/Abl-R6 (black) and PMIBcr/Abl-R6 (red) at 20 µM in 20 mM phosphate buffer, pH 7.4, obtained on a Jasco spectrometer at 25 °C. Proteins were quantified spectroscopically by UV measurements at 280 nm using a molar extinction coefficient of 9970 calculated as described [67]. Percent helicity was calculated from the ratio of [θ]222 to [θ]max, where [θ]max = −39500 × [1−(2.57/n)] [68].
