Figure 1.
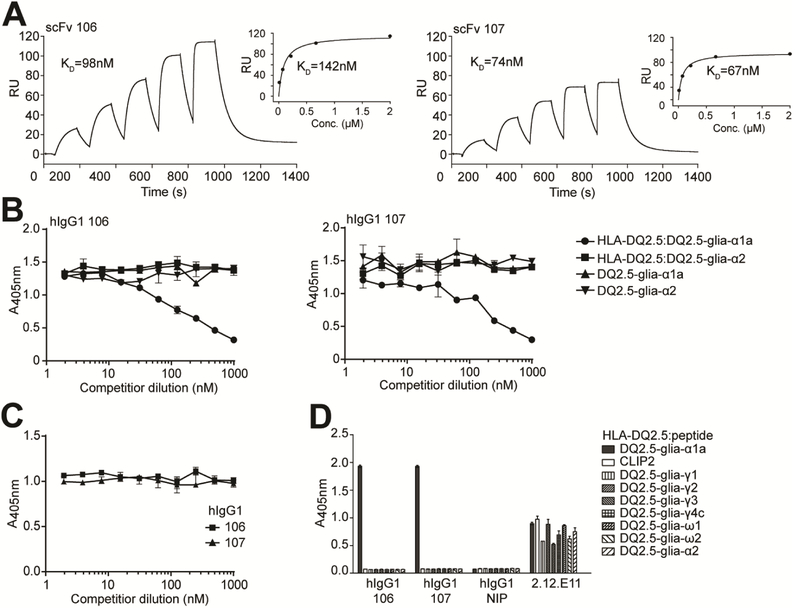
Binding properties of the lead HLA-DQ2.5:DQ2.5-glia-αIa-specific binders. (A) Representative SPR single-cycle kinetics sensorgrams of the lead scFv clones 106 and 107 for binding to HLA-DQ2.5:DQ2.5-glia-αIa (n=2–3). KD values were derived by fitting the data to a 1:1 Langmuir model. Steady state affinity evaluations are shown as inset figures. (B-D) The scFv clones and isotype control scFv (anti-NIP) were reformatted to hIgG1 mAbs, expressed and purified before assessment of specificity. (B,C) Competition ELISAs where the hIgG1 mAbs were pre-incubated with titrated amounts of (B) soluble pMHCs, HLA-DQ2.5:DQ2.5-glia-α1a and HLA-DQ2.5:DQ2.5-glia-α2, or the corresponding free peptides, and (C) 33mer α-gliadin before assessment of ability to compete with binding to plate-bound HLA-DQ2.5:DQ2.5-glia-α1a (n=3). (D) Eight different HLA-DQ2.5:gluten peptide complexes and HLA-DQ2.5:CLIP2 were used in ELISA for specificity analysis (n=2). mAb 2.12.E11 specific for the β-chain of HLA-DQ2 was included to control pMHC capture levels. Error bars illustrate mean ± SD of duplicates.