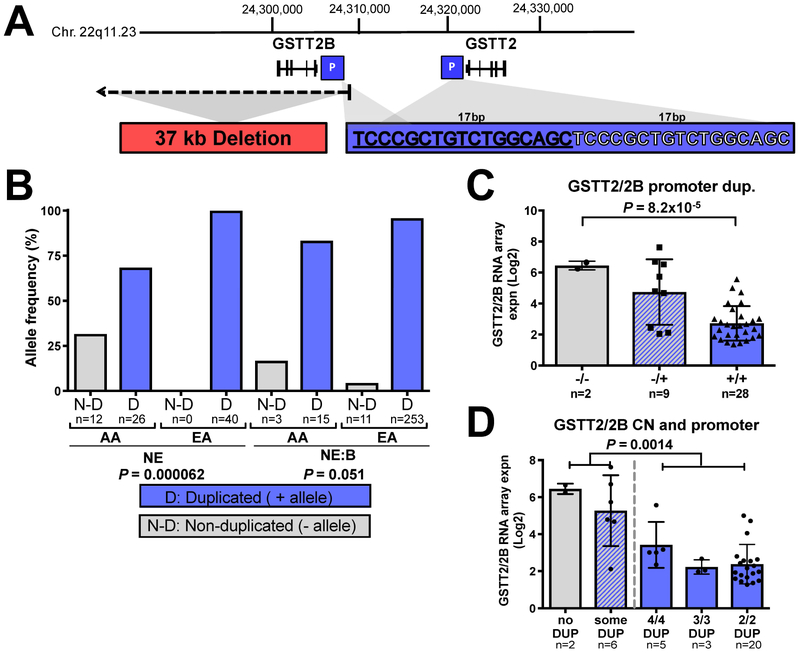
Figure 2. GSTT2/2B 17bp promoter duplication is associated with reduced mRNA expression.
(A) Two genomic events influence GSTT2/2B mRNA levels: a 37kb deletion that removes the GSTT2B gene, and the 17bp tandem GSTT2/2B promoter duplication. (B) The 17bp GSTT2/2B promoter duplication frequency is significantly lower in AA vs. EA NE (non-disease) populations, with a similar trend between NE:BE disease groups by Fisher Exact test. Allele numbers are shown below each bar. (C) When all squamous samples are combined and analyzed (one-way ANOVA, with a post-test for linear trend P value of 0.00078) we observed that the 17bp promoter duplication shows a dose-dependent association with GSTT2/2B mRNA expression. (D) The combination of the 17bp GSTT2/2B promoter duplication with the gene-dose effect of the GSTT2B whole gene deletion shows that individuals with only (homozygous) the 17bp promotor duplication had lower expression as compared to individuals having at least one copy of the non-duplicated promoter, irrespective of how many GSTT2 copies they have. We used a student T-test and Mann-Whitney tests to compare genotypes that included at least one non-duplicated 17bp allele (first 2 bars) to those with only alleles containing 17bp duplicated GSTT2 promotors (3 bars on the right). We quote the MWU P value as it was more conservative than the two-sample T-test (P=0.00004).