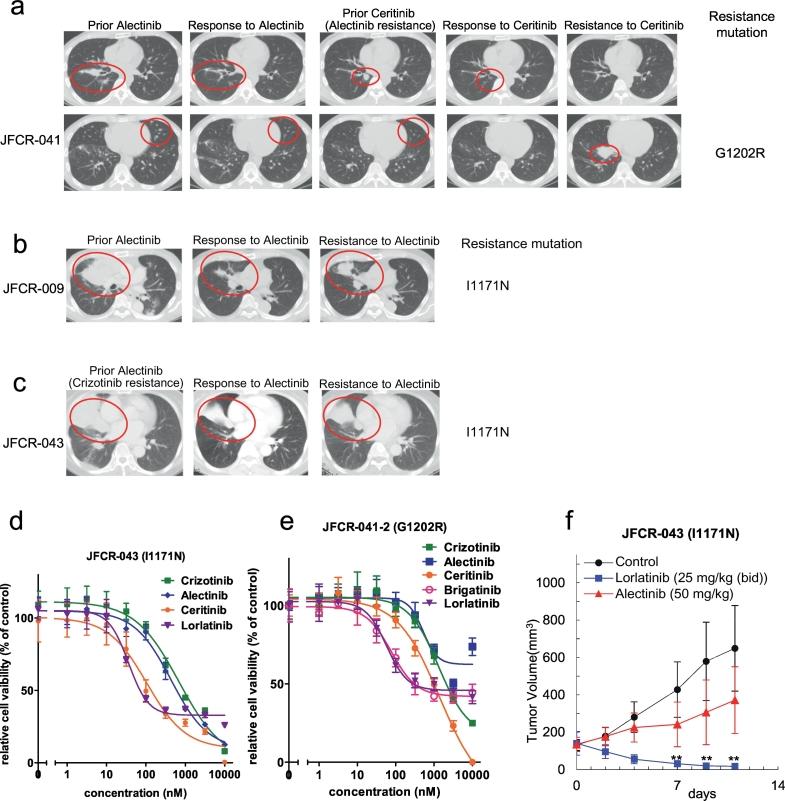
Fig. 1.
Resistance mechanisms in alectinib refractory patients.
(a–c) Computed tomographic images of JFCR-041, 009 and 043 patients at baseline and at the time of relapse. Identified resistance mutations are indicated in the figures. (d) Patient-derived JFCR-043 cancer cells (EML4-ALK-I1171N) were treated with the indicated concentration of crizotinib, alectinib, ceritinib, or lorlatinib for 72 h. Cell viability was analyzed using the CellTiter-Glo assay. (e) Patient-derived JFCR-041-2 cells (EML4-ALK-G1202R) were treated with the indicated concentration of crizotinib, alectinib, ceritinib, brigatinib, or lorlatinib for 72 h. Cell viability was analyzed using the CellTiter-Glo assay. (f) JFCR-043 cells were subcutaneously implanted into BALB-c nu/nu mice. After the tumor volume reached approximately 200 mm3, the mice were randomized into vehicle, lorlatinib (PF-06463922) 25 mg/kg, or alectinib 50 mg/kg (each group n = 6) and treated once daily by oral gavage for 5 to 6 days/week. The tumor size was measured twice weekly. Results are expressed as mean ± SD.