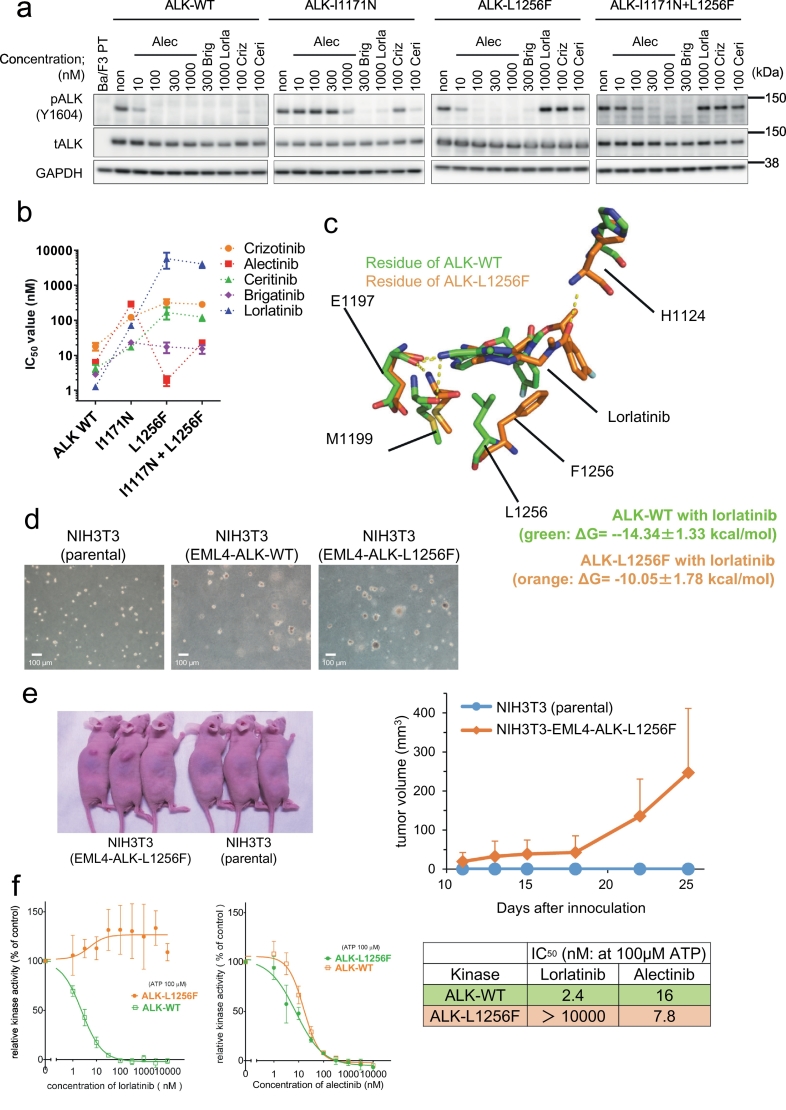
Fig. 6.
ALK-L1256F single mutation has a tumorigenicity, and is resistant to lorlatinib but sensitive to alectinib.
(a) Suppression of phospho-ALK in Ba/F3 EML4-ALK wild-type poly clonal cells, Ba/F3 I1171N#12 cells, and Ba/F3 cells with re-induced ALK-L1256F or I1171N + L1256F. The cells were treated with the indicated concentration of ALK-TKIs. (b) Calculated IC50 values of the re-induced L1256F single or I1171N + L1256F double mutated Ba/F3 poly clonal cells. These cells were treated with crizotinib, alectinib, ceritinib, brigatinib, or lorlatinib for 72 h. Results are expressed as mean ± SD. (c) MD-relaxed structures of alectinib-bound ALK-WT (green),or L1256F single (orange). L/F1256, and lorlatinib in an energetically stable conformation obtained from five sets of 50 ns simulations are depicted by sticks (green/orange, carbon; blue, nitrogen; red, oxygen). Average ΔG values (from three sets of the free energy simulations) are indicated. (d) The results of soft agar colony formation assay to NIH3T3cells (left: parental, middle: EML4-ALK-WT, and right: EML4-ALK-L1256F). The scale bar indicated 100 μm. (e) In vivo tumorigenesis assay of NIH3T3 expressing EML4-ALK-L1256F. Tumorigenesis was confirmed in 4/4 mice. A picture of 3 representative mice (left) and its growth curve (right). (f) The evaluation of the inhibitory activity of lorlatinib and alectinib to WT or L1256F mutated ALK in the in vitro kinase assay using the ADP-Glo Assay kit. Alectinib, but not lorlatinib, showed a dose-dependent inhibition of ALK-L1256F mutant activity. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)