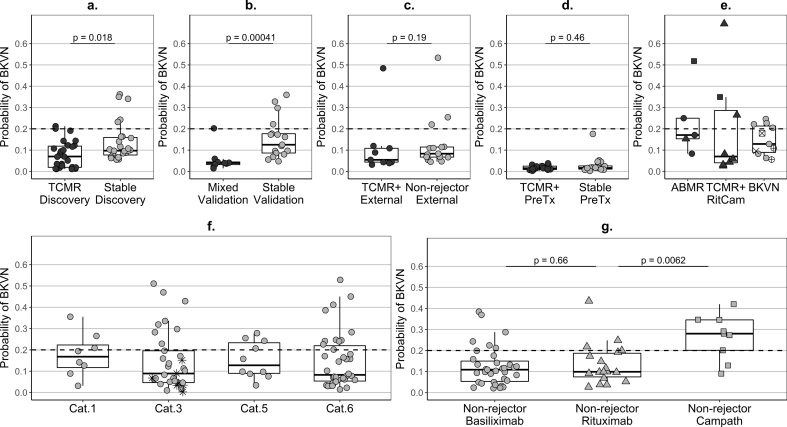
Fig. 6.
Predicted probability of BK-virus nephropathy in kidney transplant recipients.
Predicted probability – (a,e) calculated as the median of the set of probabilities estimated for each patient of the development dataset in the 50 repeats of the cross-validation cycles (Step 12 of Note 1 in Supplementary Discussion) or (b,c,d,f,g) based on the newly-developed six-gene signature (Supplementary Fig. S11); ABMR – antibody-mediated rejection (category 2 according to Banff’09 classification); BKVN – BK virus nephropathy (confirmed with a specialised histological staining); TCMR – T-cell-mediated rejection (category 4); Mixed – histological features of both, ABMR and TCMR; TCMR+ − patients with TCMR only or with mixed-type histology; Stable – patients fulfilling the inclusion and exclusion criteria listed in Table 1; Non-rejector – patients not fulfilling the selection criteria in Table 1 but without clinical or histological evidence of TCMR, ABMR or BKVN up to day 400 post-transplantation; dot colour: black – rejectors, grey – stable or non-rejector patients; dot shape - induction agent in KALIBRE patients: circle – Basiliximab, triangle – Rituximab, square – Alemtuzumab; dotted lines - cut-off 0.2 for dichotomous classification of the probability of BKVN; samples: rejectors - single pre-biopsy sample, BKVN –single near-biopsy sample, stable/non-rejector patients – summary (median per patients) of longitudinal samples covering between days four and 400 post transplantation; (a) Discovery – training patients used in TCMR signature development (TCMR (n = 27) fulfilling the inclusion and exclusion criteria listed in Table 1 and stable patients (n = 27)); (b) Validation – test patients from the KALIBRE study used for TCMR signature validation (Mixed-type rejectors (n = 9) and new stable patients (n = 17)); (c) External – patients from the independent trial EMPIRIKAL used for TSMR signature validation (rejectors (n = 9) with TCMR or Mixed-type histology and non-rejectors (n = 15)); (d) PreTx – cross-sectional pre-transplantation samples - one per patient from rejectors with TCMR (n = 16) and Mixed-type (n = 2) histology and training stable patients from the signature development dataset (n = 20); (e) ABMR rejectors (n = 5), RitCam rejectors with alternative induction and TCMR (n = 6) or Mixed-type (n = 2) histology; BKVN patients: grey dots BKVN (n = 7) included in the BKVN signature development dataset, crossed dots BKVN: +dot (n = 2) excluded from the training dataset due to prior suspected TCMR or some genes missing, x-dot (n = 1) Alemtuzumab induction, x (n = 1) a patient from the EMPIRICAL trial; (f) – cross-sectional pre-biopsy samples (up to 15 days prior to the first post-transplantation biopsy (median two days) and a single one at 25 days) from patients which did not show features of rejection at least up to three months post biopsy; Cat – histological category according to Banff’09 classification (Cat.1 – normal (n = 8, three (38%) BKVN-positive), Cat.3 – borderline changes (n = 33, eight (24%) BKVN-positive), Cat.5 - interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy (n = 10, four (40%) BKVN-positive), Cat.6 – other non-rejection histology (n = 38, 11 (29%) BKVN-positive)); star dots (*) – patients with histological features of borderline changes treated for rejection due to clinical considerations; (g) – summary (median per patient) of longitudinal validation follow-up samples from non-rejectors with different induction agents: Basiliximab induction (n = 35, six (17%) BKVN-positive median), Rituximab (n = 18, four (22%) BKVN-positive), Alemtuzumab (n = 9, seven (78%) BKVN-positive median); p-values derived from a Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney tests.