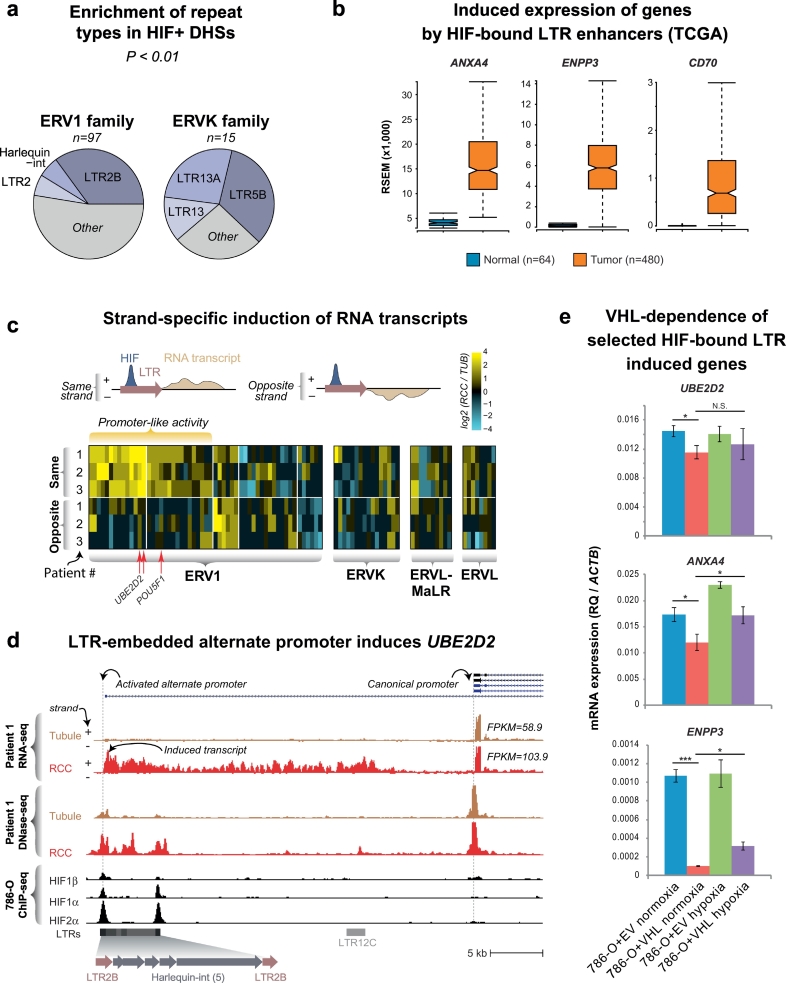
Fig. 7.
Activation of cryptic LTR-derived promoters in RCC.
(a) Enrichment of HIF-bound DHS in LTR families. The ERV1 and ERVK families of LTR show significant enrichment for HIF-bound DHSs. Of these, the LTR2B subfamily shows the greatest number of HIF-bound DHSs (n = 34).
(b) TCGA expression of selected genes putatively induced by HIF-bound cryptic promoters in LTRs. The ends of the bar plots represent the 25th and 75th quartiles with whiskers representing 1.5× inter-quartile range (10% outlier trim applied for clarity). All tumor-normal comparisons are significant (p < 1 × 10−10) by one-tailed t-test.
(c) HIF-bound DHSs in LTRs show strand-specific induction of RNA transcripts. Since LTRs are intrinsically directional, enumeration of RNA-seq reads up to 1 kb on either the same or opposite strand of the LTR identifies elements with HIF-dependent promoter-like activity (increased transcripts in RCC samples compared to tubules with the same directional orientation as the LTR). The heatmap represents the ratio of the RCC/tubule read counts for each patient on the indicated strand.
(d) A HIF-bound LTR is transcriptionally active and is associated with increased expression of the UBE2D2 gene. Similar to the alternate POU5F1 promoter, some of the HIF-bound LTRs that show promoter-like activity drive the expression of novel transcripts and increase the expression of nearby genes. Shown is the expression of UBE2D2 transcripts, which increases 1.76× in Patient 1's RCC compared to its matched tubule control.
(e) HIF-bound LTR-induced genes exhibit HIF-dependence. RT-PCR primers were used to quantify the indicated transcripts in 786-O cells stably transduced with VHL (786-O + VHL) or empty vector (786-O + EV) cultured in normoxia or hypoxia (2% O2) for 24 h. Expression levels (relative quantification, RQ) were calculated using the β-actin housekeeping gene (ACTB). N.B. expression scale differences between the canonical and novel transcripts. Error bars indicate standard deviations of three experimental replicates. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.005, N.S. not significant (two-tailed t-test).