Figure 3. Cholinergic inputs to the RTN.
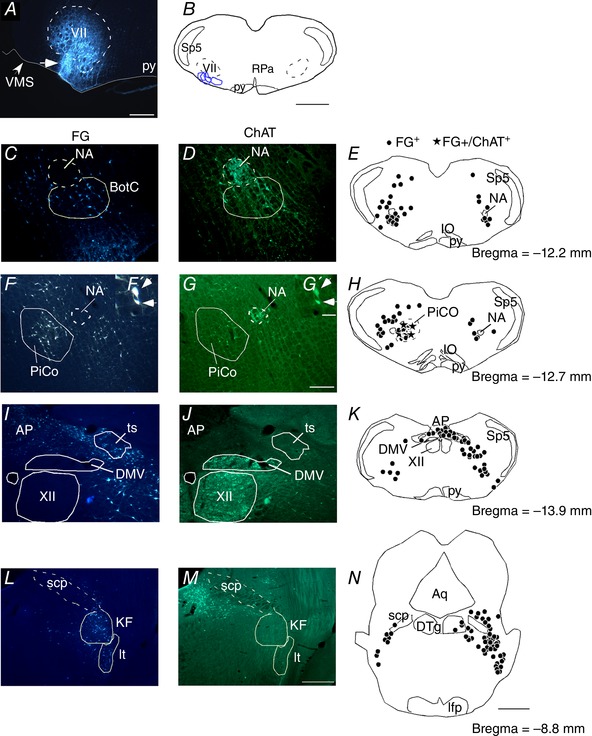
A, photomicrography showing the location of an individual FG injection into the RTN. B, schematic drawing depicting the location of all FG injections into the RTN (n = 4). C–N, FG injections into the RTN‐labelled neurons that were immunoreactive for ChAT (ChAT‐ir) in the nucleus ambiguous and Bötzinger complex (NA‐BötC) (C–E), PiCo F–F′, G–G′ and H), dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus (DMV) (I–K) and intertrigeminal (It) and Kolliker‐Fuse (KF) region (L–N). Aq, aqueduct mesencephalic; AP, area postrema; ts, solitary tract; BötC, Bötzinger complex; cc, central canal; DTg, dorsal tegmental nucleus; it, intertrigeminal region; NA, nucleus ambiguus; py, pyramidal tract; scp, superior cerebellar peduncle; VMS, ventral medullary surface; VII, facial motor nucleus; XII, hypoglossal motor nucleus; Sp5, spinal trigeminal nucleus; RPa, raphe pallidus. Scale bar = 300 μm in (A); 1 mm in (B) and (N); 100 μm in (G) applied to (C) to (G); 20 μm in (G′) applied to (F′) and (G′) and 200 μm in (M) applied to (I) to (M). [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
