Figure 2.
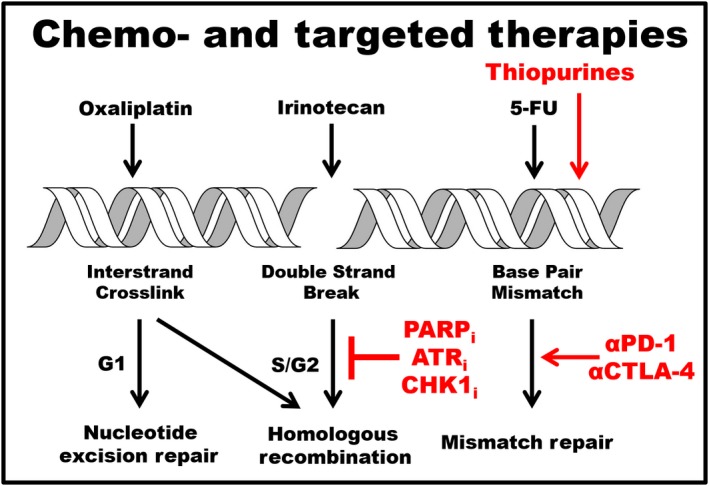
Therapies targeting cancer specific DNA repair defects. Current chemotherapy agents (black) used to treat mCRC. Oxaliplatin induces DNA interstrand cross‐links that are repaired by nucleotide excision repair proteins during G1 and by Fanconi anemia and HR proteins during S phase. Irinotecan (SN38) is a topoisomerase inhibitor that induces single (SSB)‐ and double‐strand breaks (DSBs) that are repaired by HR and BER proteins. 5‐Fluorouracil is an antimetabolite that can lead to DNA base pair mismatches repaired by the MMR pathway. Alternative therapies (red) that can be used in combination with current chemotherapy agents. PARPi and ATRi induce stalled replication forks and DSBs that are lethal in cells carrying mutations in HR genes, and CHKi block cell cycle arrest in the presence of replication stress. Chemosensitivity can be further induced in cells treated with genotoxic agents in combination with targeted therapies. Thiopurines induce DNA base pair mismatches that can lead to increased mutational and neoantigen burdens. Anti‐PD‐1 and CTLA‐4 immunotherapies target MMRd CRC tumors and are most effective against tumors with high neoantigen burdens.
