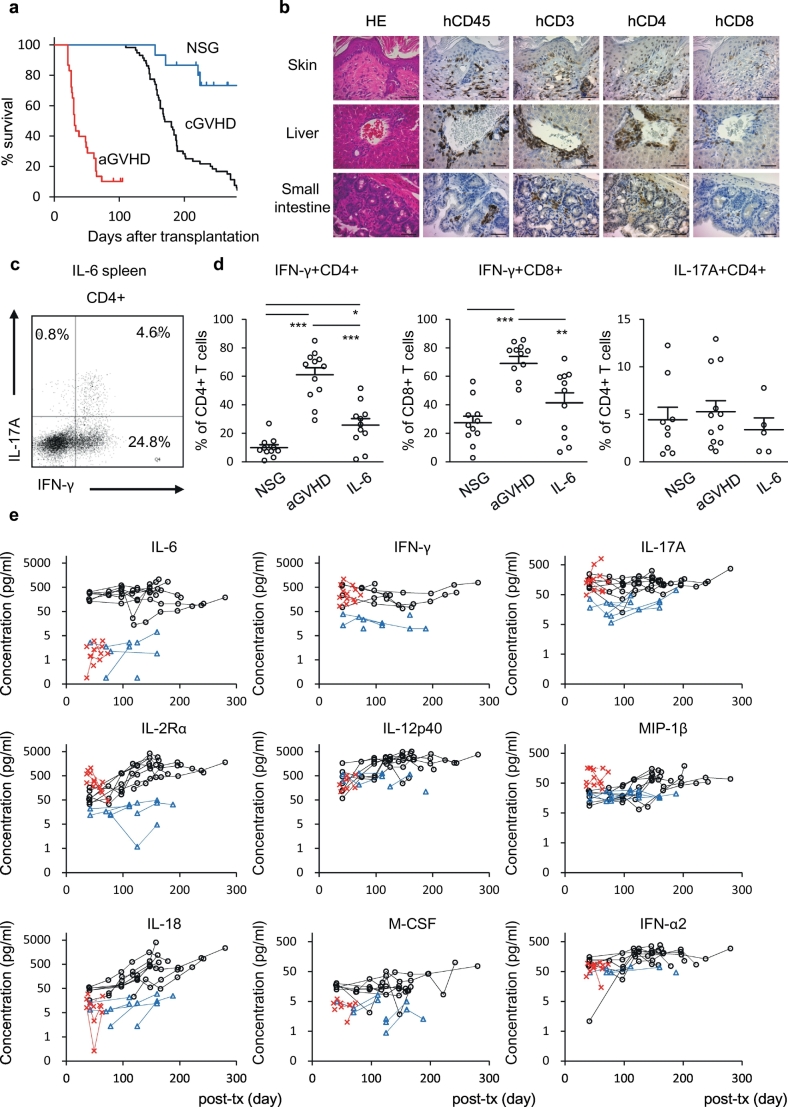
Fig. 3.
Comparison between hIL-6 Tg NSG cGVHD humanised mice and human aGVHD humanised mice.
(a) Kaplan-Meier plot showing reduced survival of both cGVHD humanised mice (n = 58, black) and aGVHD humanised mice (n = 26, red) compared with non-Tg NSG humanised mice (n = 15, blue) (cGVHD vs. non-Tg, p = 0.000225; aGVHD vs. non-Tg, p = 1.68 × 10−7; cGVHD vs. aGVHD, p = 2.11 × 10−22 by log-rank test). (b) Histological analyses of skin, liver and small intestine of an aGVHD humanised mouse (acute#A-1). Bars: (far left) 100 μm; (the others) 50 μm. (c) Representative flow cytometry plots of a cGVHD humanised mouse (IL6#2-1). (d) Frequency of IFN-γ and IL-17A producing splenic T cells in non-Tg NSG humanised mice (NSG-IFN-γ+, n = 11, NSG-IL-17A+, n = 9), aGVHD humanised mice (aGVHD: n = 12), and cGVHD humanised mice (IL6-IFN-γ+, n = 11, IL6-IL-17A+, n = 5). *P = 0.005, **P = 0.004, ***P < 0.0001 by 1-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test. Error bars represent mean ± SEM. (e) Plasma cytokine/chemokine concentration of cGVHD humanised mice (Black: IL-6, n = 8), aGVHD humanised mice (Red: aGVHD, n = 6) and non-Tg NSG humanised mice (Blue: NSG, n = 5). (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)