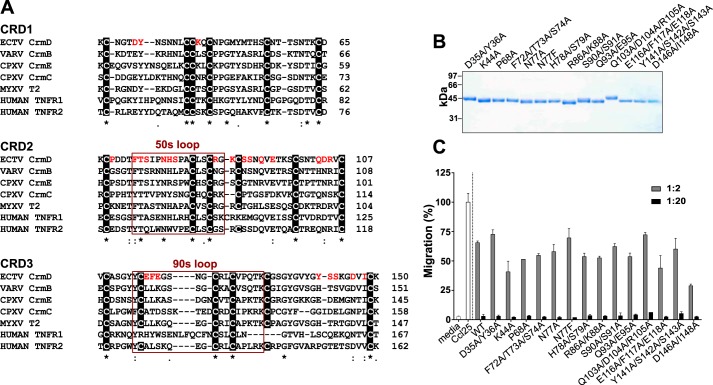
Figure 3.
CrmD site-directed mutagenesis. A, Clustal Omega alignment of the amino acid sequences of the first three CRDs of the vTNFRs CPXV CrmE (gene K3R, strain elephantpox, UniProt/TrEMBL accession number Q9DJL2), CPXV CrmC (gene CPXV191, strain Brighton Red, UniProt/TrEMBL accession number Q9YP87), ECTV CrmD (gene E6, strain Hampstead, UniProt/TrEMBL accession number 057300), VARV CrmB (gene G2R, strain Bangladesh 1975, UniProt/TrEMBL accession number P34015), and MYXV T2 (gene m002L, strain MAV, UniProt/TrEMBL accession number E2CZP3) and the human TNFRs TNFRl (gene TNFRSFlA, UniProt/TrEMBL accession number P19438) and TNFR2 (gene TNFRSFlB, UniProt/TrEMBL accession number P20333). CrmD residues subjected to mutagenesis are highlighted in red. Sequences corresponding to the 50s and 90s loops are framed in red and labeled accordingly above the frame. Conserved cysteines are shown in a black background. Numbers at the end of each line indicate the amino acid position of the last residue in the line relative to the complete sequence of the protein. B, Coomassie Blue–stained gel showing the SDS-PAGE analysis of 1 μl of the protein stock purified for each mutant. Molecular mass is shown in kDa. C, inhibition of mouse Ccl25-induced chemotaxis of MOLT-4 cells by CrmD WT or the indicated mutants. 70 nm chemokine was preincubated in the absence or presence of recombinant protein at increasing chemokine:protein molar ratios (see legend), and its ability to induce transwell migration of MOLT-4 cells was assessed. Migrated cells were detected by measuring the A490 using a Cell Titer Aqueous One Solution kit. Data are represented as the percentage relative to the A490 detected when the cells were incubated with the chemokine alone (Cc125). Media indicates the cell migration recorded in the absence of chemokine. Results are shown as mean ± S.D. (error bars) of triplicates from one experiment representative of three independent experiments.