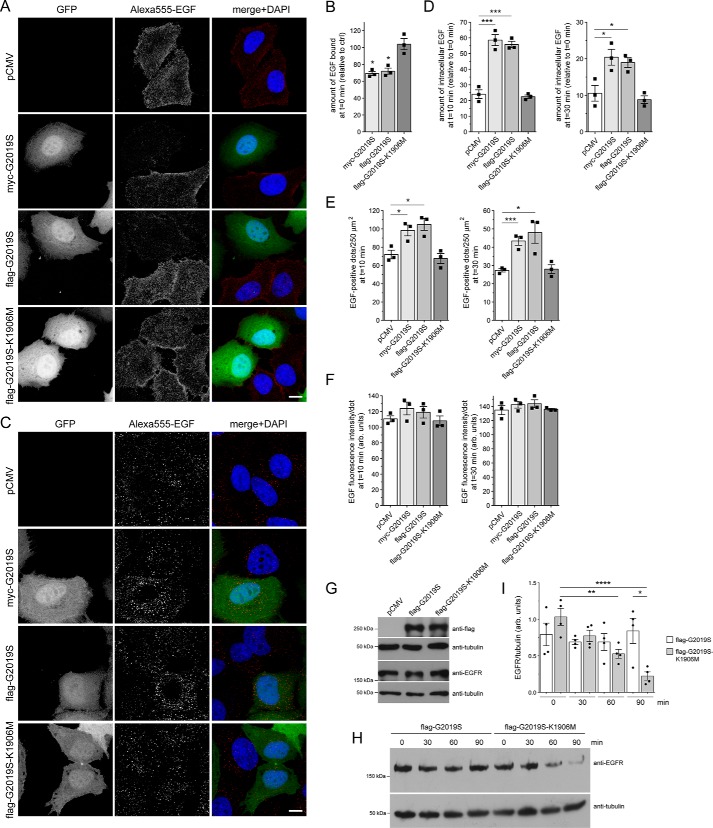
Figure 1.
Pathogenic G2019S LRRK2, but not a kinase-inactive G2019S-K1906M variant, causes a deficit in EGF binding and degradation. A, HeLa cells were transfected with either pCMV or cotransfected with GFP and either myc-tagged G2019S LRRK2, FLAG-tagged G2019S, or G2019S-K1906M LRRK2 as indicated; incubated with Alexa555-EGF for 30 min at 4 °C; washed to remove unbound fluorescent EGF; and fixed and processed as described under “Materials and methods.” Scale bar, 10 μm. B, quantification of surface-bound fluorescent EGF (t = 0 min) of cells transfected with the various constructs as indicated and normalized to EGF surface binding of pCMV-transfected cells (ctrl). n = 3 independent experiments. *, p < 0.05. C, HeLa cells transfected with the indicated constructs were allowed to bind Alexa555-EGF at 4 °C, washed to remove unbound fluorescent EGF, and then shifted to 37 °C for 10 min to allow for the internalization and degradation of fluorescent EGF. Scale bar, 10 μm. D, quantification of Alexa555-EGF was performed after 10 (left) and 30 min (right) upon internalization and normalized to the amount of Alexa555-EGF binding for each condition at t = 0 min, thus reflecting the percentage of internalized bound fluorescent EGF. n = 3 independent experiments. *, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.005. E, quantification of the total number of fluorescent EGF-positive puncta per 250 μm2 upon expression of distinct constructs as indicated after 10 (left) and 30 min (right) of internalization. n = 3 independent experiments. *, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.005. F, because the immunofluorescence signal intensity directly correlates to the size of the individual structures, signal intensity per punctum was quantified at 10 (left) and 30 min (right) upon internalization, which revealed no change among the different conditions, further indicating a deficit in EGF degradation rather than an increase in the amount of internalized fluorescent EGF per cell. G, HEK293T cells were transfected with the indicated constructs followed by analysis of endogenous EGFR expression levels. H, HEK293T cells were transfected with either pathogenic G2019S LRRK2 or with kinase-inactive G2019S-K1906M variant and serum-starved for 1 h in the presence of cycloheximide to block novel protein synthesis, and EGFR internalization was stimulated with nonlabeled EGF for the indicated time points. Cell extracts were analyzed by Western blotting for EGFR levels, and tubulin was used as a loading control. I, quantification of EGFR degradation in HEK293T cells transfected with either G2019S LRRK2 or G2019S-K1906M, at distinct time points as indicated, and with values normalized to tubulin as a loading control. n = 4 independent experiments. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ****, p < 0.001. All error bars represent S.E.M.