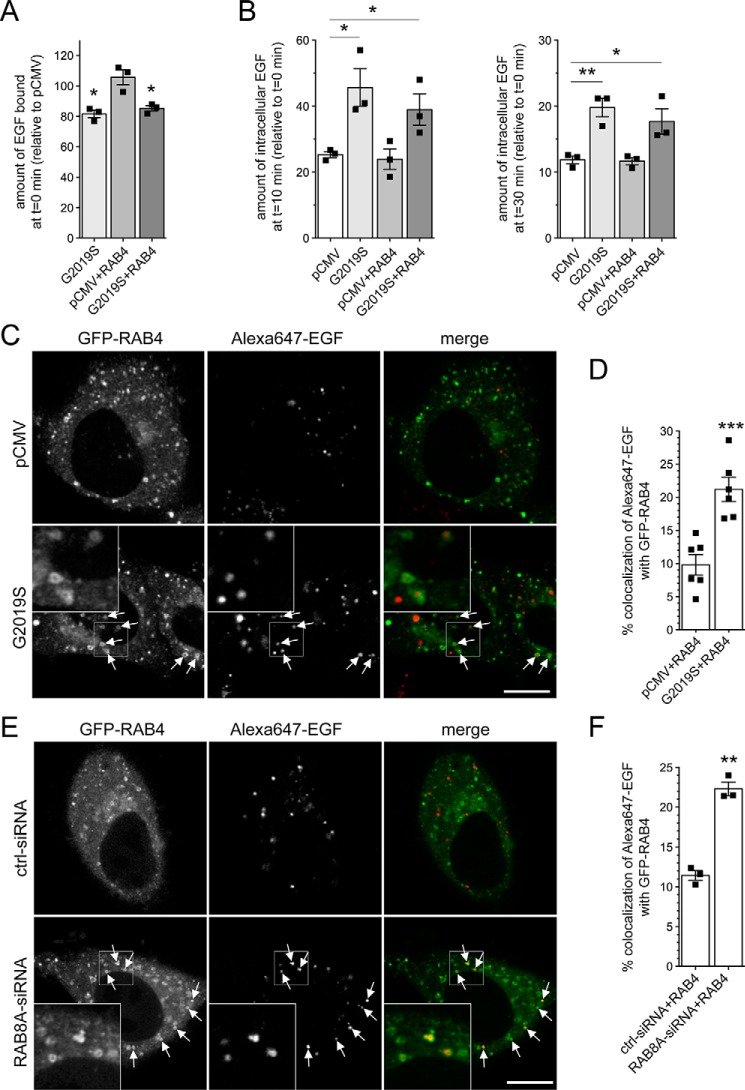
Figure 6.
Pathogenic LRRK2 or knockdown of RAB8A causes accumulation of EGF in a RAB4-positive endocytic compartment. A, HeLa cells were transfected with either empty pCMV vector or pathogenic LRRK2 or cotransfected with GFP-tagged RAB4, and surface-bound fluorescent EGF was quantified. n = 3 independent experiments. *, p < 0.05. B, cells were transfected as indicated followed by quantification of internalized fluorescent EGF at 10 (left) and 30 min (right). n = 3 independent experiments. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01. C, example of HeLa cells cotransfected with GFP-RAB4 and either empty pCMV vector or pathogenic LRRK2. Live pictures were taken 20 min upon fluorescent EGF internalization, and arrows point to GFP-RAB4–positive vesicles containing Alexa647-EGF. Scale bar, 10 μm. D, quantification of colocalization of Alexa647-EGF with GFP-RAB4 (Manders' coefficient 1 × 100) from 15–20 cells per experiment. n = 6 independent experiments. ***, p < 0.005. E, example of HeLa cells cotransfected with GFP-RAB4 and either ctrl-siRNA or RAB8A-siRNA. Live pictures were taken as described above. Arrows point to GFP-RAB4–positive vesicles containing Alexa647-EGF. Scale bar, 10 μm. F, quantification of colocalization of Alexa647-EGF with GFP-RAB4 (Manders' coefficient 1 × 100) from 15–20 cells per experiment. n = 3 independent experiments. **, p < 0.01. All error bars represent S.E.M.