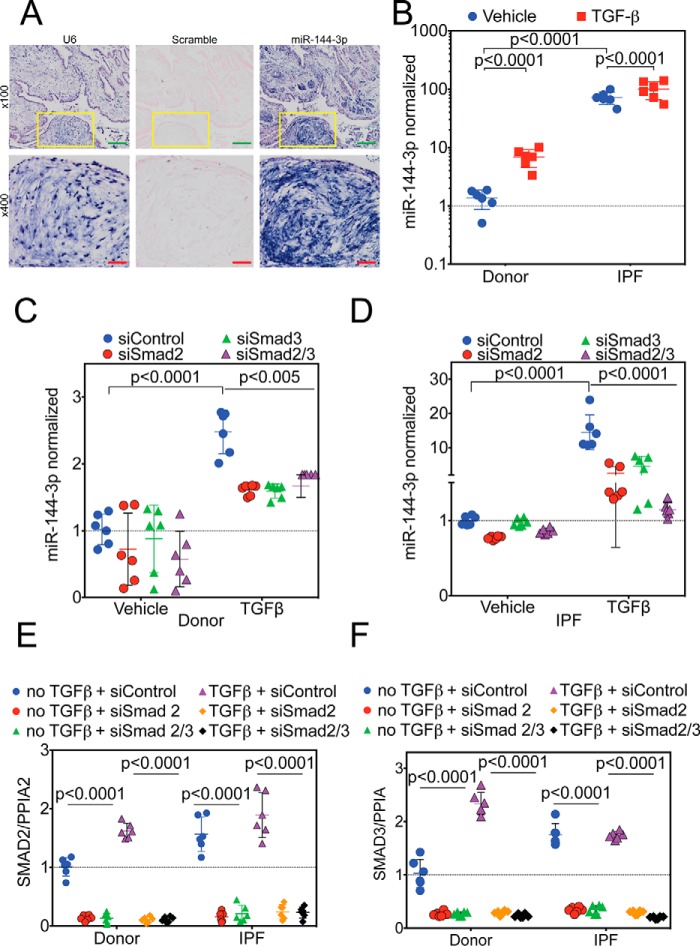
Figure 4.
Regulation of miR-144-3p expression. A, lung biopsies were obtained from IPF subjects (n = 5). In situ hybridization was performed as described employing probes directed against U6 (left), scrambled control (center), or miR-144-3p (right). Low power images are shown on the top. Yellow inset squares are magnified at the bottom. Green inset bar = 200 μm and red inset bar = 50 μm. B, donor and IPF lung fibroblasts were stimulated with and without TGFβ, and RNA was isolated for qPCR. Significantly higher levels (>70-fold) of miR-144-3p were detected in IPF lung fibroblasts compared with donor controls (p < 0.0001, n = 6). TGFβ stimulation increased expression of miR-144-3p in donor lung fibroblasts by ∼5-fold (p < 0.0001), whereas it increased by ∼1.4-fold (p < 0.0001) in IPF lung fibroblasts. Data were log-transformed and analyzed by two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test. C, donor lung fibroblasts were incubated with Smad2 and/or Smad3 siRNA and stimulated with TGFβ. TGFβ significantly increased miR-144-3p expression in the presence of the scrambled control (p < 0.0001, n = 6). Smad2 and/or Smad3 siRNA significantly decreased the effect of TGFβ on miR-144-3p expression (p < 0.005, n = 6). Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey's post hoc test. D, IPF lung fibroblasts were incubated with Smad2 and/or Smad3 siRNA and stimulated with TGFβ. TGFβ significantly increased miR-144-3p expression in the presence of the scrambled control (p < 0.0001, n = 6). Smad2 and/or Smad3 siRNA significantly decreased the effect of TGFβ on miR-144-3p expression (p < 0.0001, n = 6). Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey's post hoc test. E and F, quantitative RT-PCR for Smad2 (E) and Smad3 (F) for experiments in C and D. Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test.