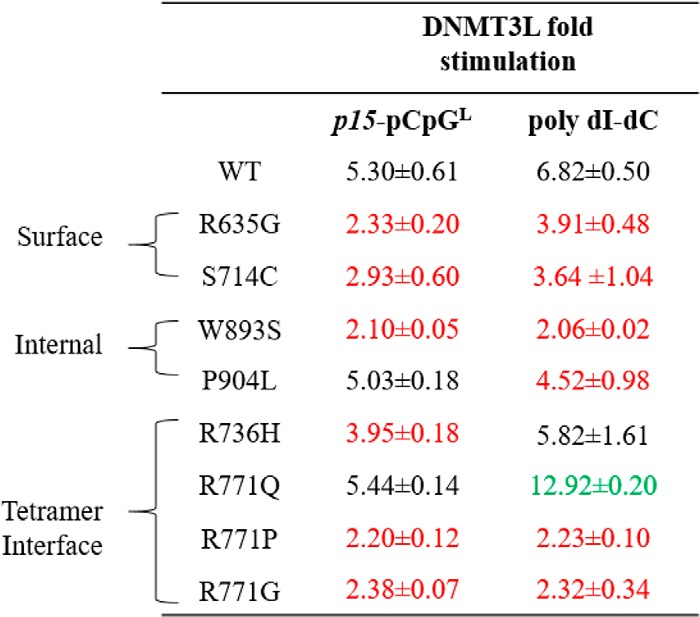
Table 3.
Fold stimulation by DNMT3L for wildtype and AML patient-derived DNMT3A mutants using poly(dI-dC) and p15-pCpGL DNA substrates
Fold stimulation was determined by the sum of product formed by DNMT3A with DNMT3L divided by product formed by DNMT3A without DNMT3L. DNMT3L, known to interact at the tetramer interface of DNMT3A, leads to varying levels of responsiveness for tetramer interface and internal mutations, but comparable reduced stimulation in surface mutations. All DNMT3As were at 150 nm tetramer, corresponding to 27 nm active tetramer enzyme (24). DNA substrate concentrations were: 5 μm bp for poly(dI-dC) and 10 μm bp for p15-pCpGL plasmid. Wildtype and DNMT3A mutants were preincubated with DNMT3L (1:1) for 1 h at 37 °C prior to initiating the reaction by the addition of substrate DNA. Mutations are categorized based on their respective location within the DNMT3A catalytic domain (red corresponds to decreased stimulation and green corresponds to increased stimulation, compared to wildtype). Data reflect the results from at least three independent DNMT3A–DNMT3L co-incubation reactions.