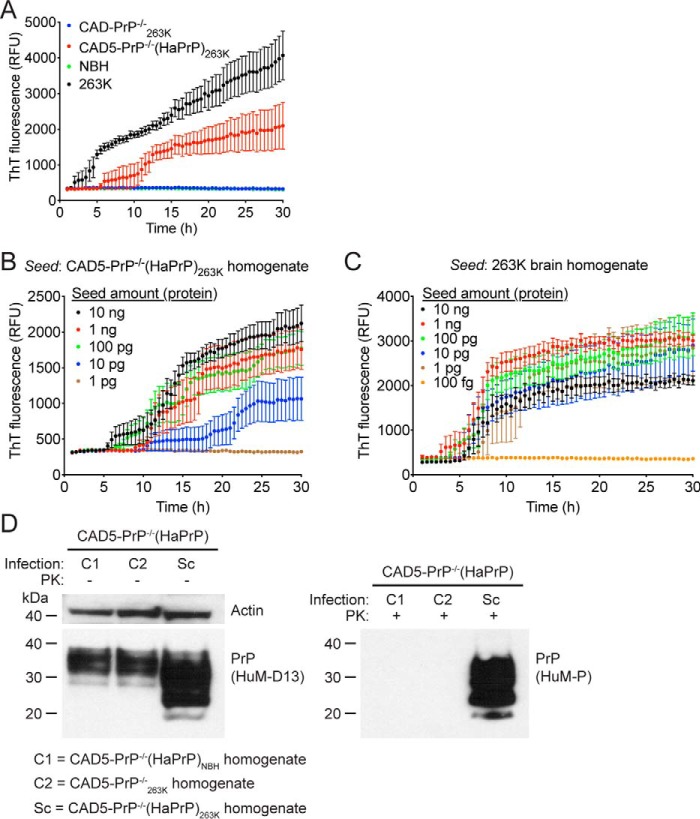
Figure 4.
Prion seeding activity and cellular infectivity of 263K prions passaged in CAD5-PrP−/−(HaPrP) cells. A, RT-QuIC using recombinant HaPrP(23–231) as a substrate and 100 ng of NBH (green), 263K-infected hamster brain homogenate (black), or homogenate from either 263K-exposed CAD5-PrP−/− (blue) or CAD5-PrP−/−(HaPrP) (red) cells (passage seven post infection) as a seed. Each data point represents the mean ± S.E. of quadruplicate reactions. B, RT-QuIC on 10-fold serial dilutions of CAD5-PrP−/−(HaPrP)263K homogenate (passage eight). Each data point represents the mean ± S.E. of eight independent reactions. C, RT-QuIC on 10-fold serial dilutions of 263K-infected hamster brain homogenate. Each data point represents the mean ± S.E. of four independent reactions. D, infection of CAD5-PrP−/−(HaPrP) cells with cell-passaged 263K prions. Immunoblots of either undigested (left blot) or PK-digested (right blot) lysates from cells at passage seven following exposure to homogenate from either CAD5-PrP−/−(HaPrP) cells treated with NBH (C1), CAD5-PrP−/− cells treated with 263K brain homogenate (C2), or CAD5-PrP−/−(HaPrP) cells treated with 263K brain homogenate (Sc), each at passage eight. PK-resistant PrP was visualized using the antibody HuM-P, and total (undigested) PrP was detected using the antibody HuM-D13. The undigested blot was also reprobed with an antibody to actin (20–33). Molecular mass measurements are indicated in kDa.