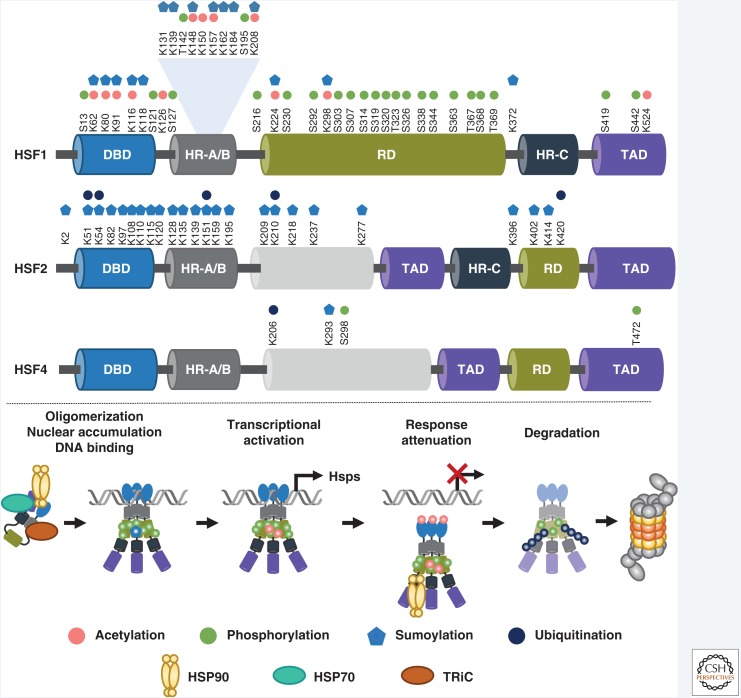
Figure 2.
Heat shock factors (HSFs) undergo a selection of posttranslational modifications (PTMs) during activation and attenuation. HSF1 is phosphorylated on multiple serine (S) and threonine (T) residues, mainly located in the regulatory domain (RD). The DNA-binding domain (DBD) and the oligomerization domain (HR-A/B) harbor lysine (K) residues that are subjected to both acetylation and sumoylation. HSF1 is also ubiquitinated, but the exact ubiquitination target lysines are not known. To date, no phosphorylatable residues have been identified in HSF2. Instead, HSF2 is sumoylated at lysine residues in DBD and HR-A/B regions. Ubiquitination of five lysine residues on HSF2 have been reported. HSF4 is also subjected to phosphorylation, sumoylation, and ubiquitination. In the absence of stimulus, HSF1 is located in the cytosol in a complex that contains chaperones (HSP90, HSP70, TRiC). Steps of activation and attenuation are accompanied by a selection of PTMs. On attenuation, HSF1 is degraded by the ubiquitin-proteasome system. HR-C, carboxy-terminal heptad repeat; TAD, transactivation domain.