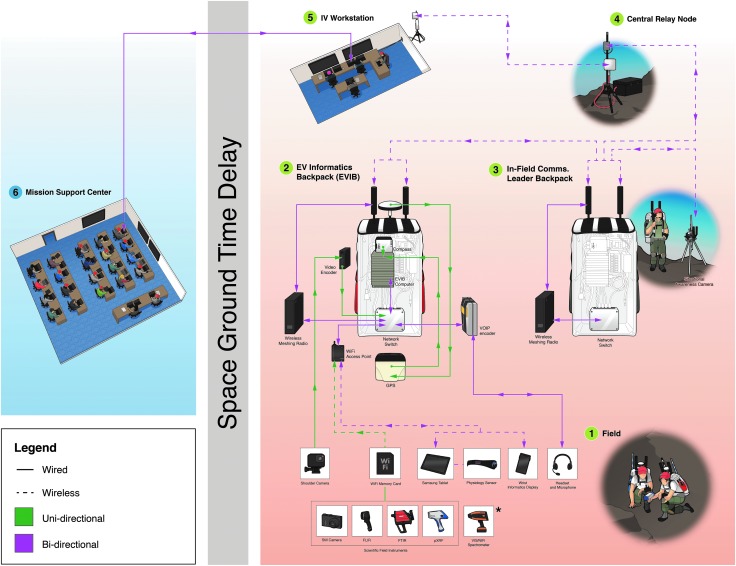
FIG. 5.
BASALT In-Field communications architecture. Fuchsia arrows represent full-duplex (two-way) data transmission, while green arrows represent unidirectional/one-way data transmission flows. Voice communications were transmitted and received by using a Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) system that converted analog audio from the EV crewmember headsets to digital audio for transmission over the network. Digital video from the chest cameras was transcoded in real time by a Teradek Cube encoder into a format that was suitable for streaming over the field network. Data from the still cameras and science instruments were sent via a WiFi SD card to the EVIB computer, where they were buffered in case of network dropouts and then forwarded over the network to servers in the IV Room and MSC. Similarly, GPS and compass data were collected by the EVIB computer and converted to a format that was suitable for sending over the field network by using the open-source gps2udp software package. *During In-Sim activities, the VIS/NIR spectrometer data was sent from the field to the MSC by capturing a still photo of the display screen output and sending the image via WiFi SD onwards per earlier description.