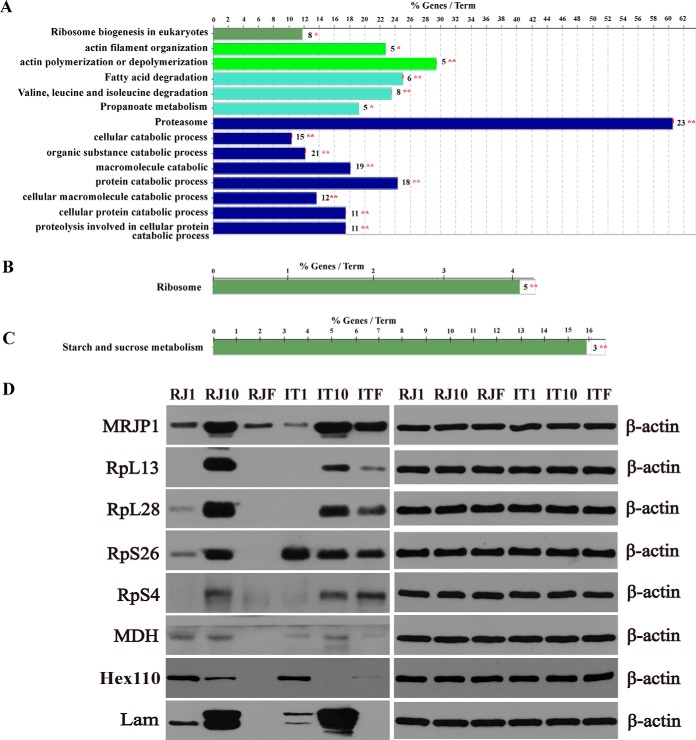
Fig. 4.
Qualitative proteome comparisons of age-specific hypopharyngeal glands (HGs) in both Italian bees (ITBs) and high royal jelly producing bees (RJBs). A, B, and C, The functional classes and pathways enriched by upregulated proteins (fold change ≥2 and p < 0.05) in newly emerged bees (NEBs), nurse bees (NBs), and forager bees (FBs), respectively. % genes/Term stands for the proportion of genes enriched in corresponding functional groups. The bars with the same color represent the same functional groups they belong to. The numbers stand for the genes enriched to the corresponding functional groups. For details of the enrichment analysis results see supplemental Table S15. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01. D, The validated abundance level change of proteins related to protein biosynthesis and energy metabolism in NEBs, NBs, and FBs by western-blotting assay. Protein β-actin is used as a loading control. RJ1, NEBs of RJBs; RJ10, NBs of RJBs; RJF, FBs of RJBs; IT1, NEBs of ITBs; IT10, NBs of ITBs; ITF, FBs of ITBs.