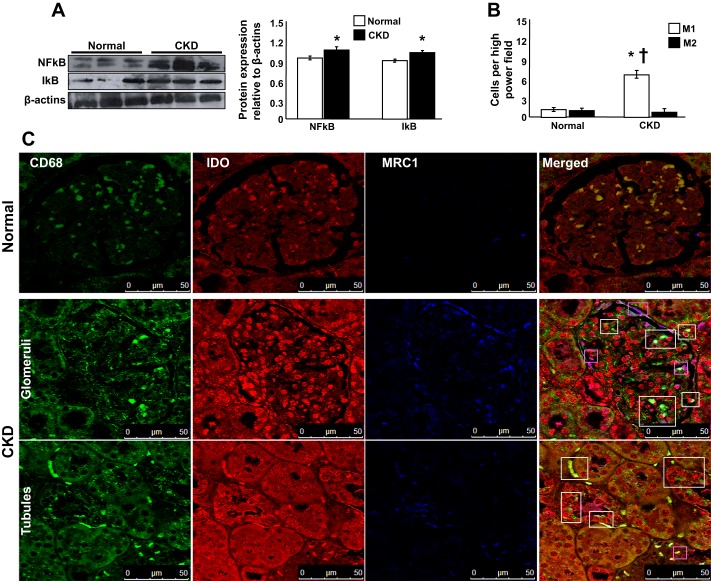
Fig. 4.
Experimental kidney disease (CKD) resulted in substantial inflammation in both kidneys. A: representative protein expression (3 bands/group) of proinflammatory NF-κB and IκB in normal pigs and pigs after 14 wk of CKD. B and C: representative quantification and pictures of renal sections costained with CD68 (total macrophages), indolamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO; M1 macrophages), manose receptor C type 1 (MRC1; M2 macrophages), and merged CD68/IDO/MRC-1 (×63) shown as examples to illustrate renal inflammatory infiltrates and identify M1 and M2 macrophages after 14 wk of CKD. The renal expression of NF-κB/IκB was increased in CKD compared with controls, whereas the presence of proinflammatory M1 macrophages (white boxes) was significantly higher than M2 (magenta boxes) in pigs after 14 wk of CKD. *P < 0.05 vs. normal; †P < 0.01 vs. M2.