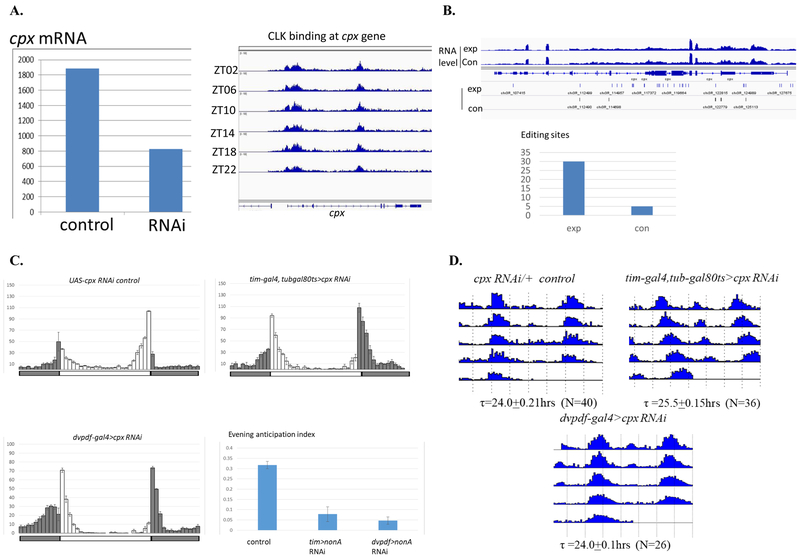
Figure 4. CPX is a Strong NonA TRIBE Target and Required for Evening Activity Anticipation.
A. RNA-seq analysis shows cpx mRNA is reduced by about 2 folds in the M- and E-cells of dvpdf>nonA RNAi line, Y axis: the FPKM reads from one reprehensive replica in the driver control and RNAi samples (left). Anti-CLK ChIP-seq suggests that CLK binds at the cpx gene locus probably with the aid of NonA and cpx RNA (right). B. CPX is a NonA TRIBE target. Top graph shows comparable cpx mRNA expression levels in the control and nonA-ADAR strains. Middle graph shows there is a dramatic increase in edit sites at the cpx locus in the nonA-ADAR strain. Each solid bar indicates an editing event. Bottom graph showed the total editing sites on the cpx transcripts as in B. C: Downregulation of CPX by the tim-gal4, tub-gal80ts or dvpdf-gal4 drivers inhibits evening activity anticipation. Experiments and behavior analysis were performed as in Figure 2. D. Down-regulation of CPX by the tim-gal4, tub-gal80ts driver lengthens the free-run period whereas CPX knockdown in the dvpdf cells has no period effect.