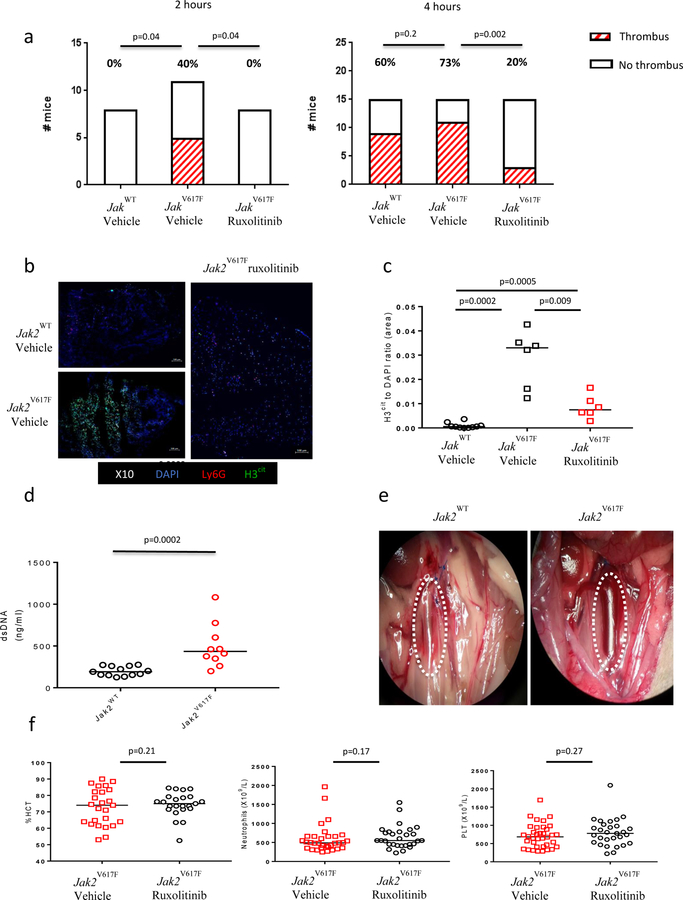
Figure 2: Jak2V617F is associated with increased venous thrombosis tendency which is reversed with ruxolitinib.
(A) Rates of thrombosis at 2 hours and 4 hours after surgical stenosis of the IVC, with animals grouped according to genotype and in vivo treatment (vehicle or ruxolitinib 90 mg/kg twice a day for 72 hours). At 2 hours: Jak2WT vehicle n=8, Jak2V617F vehicle n=11, Jak2V617F ruxolitinib n=8. At 4 hours: Jak2WT vehicle n=15, Jak2V617F vehicle n=14, Jak2V617F ruxolitinib n=14. (B) A representative image at 2 hours after IVC stenosis in a Jak2WT and a Jak2V617F mouse. (C) dsDNA plasma concentration in Jak2WT (n=13) and Jak2V617F (n=10) mice subjected to partial stenosis of the IVC. (D) Neutrophil infiltration and NET content of sections of thrombi harvested at 4 hours after IVC stenosis, as shown by neutrophil-specific Ly6G (red) and H3cit (green), respectively. DAPI is shown in blue. Scale bar=100 μm. (E) The percentage of cells (DAPI) staining positively for H3cit in thrombi harvested at 4 hours after IVC stenosis. (F) The hematocrit (HCT), neutrophil count, and platelet count (PLT) in Jak2V617F mice after 72 hours of treatment with vehicle (n=36) or ruxolitinib 90 mg/kg twice a day (n=29).