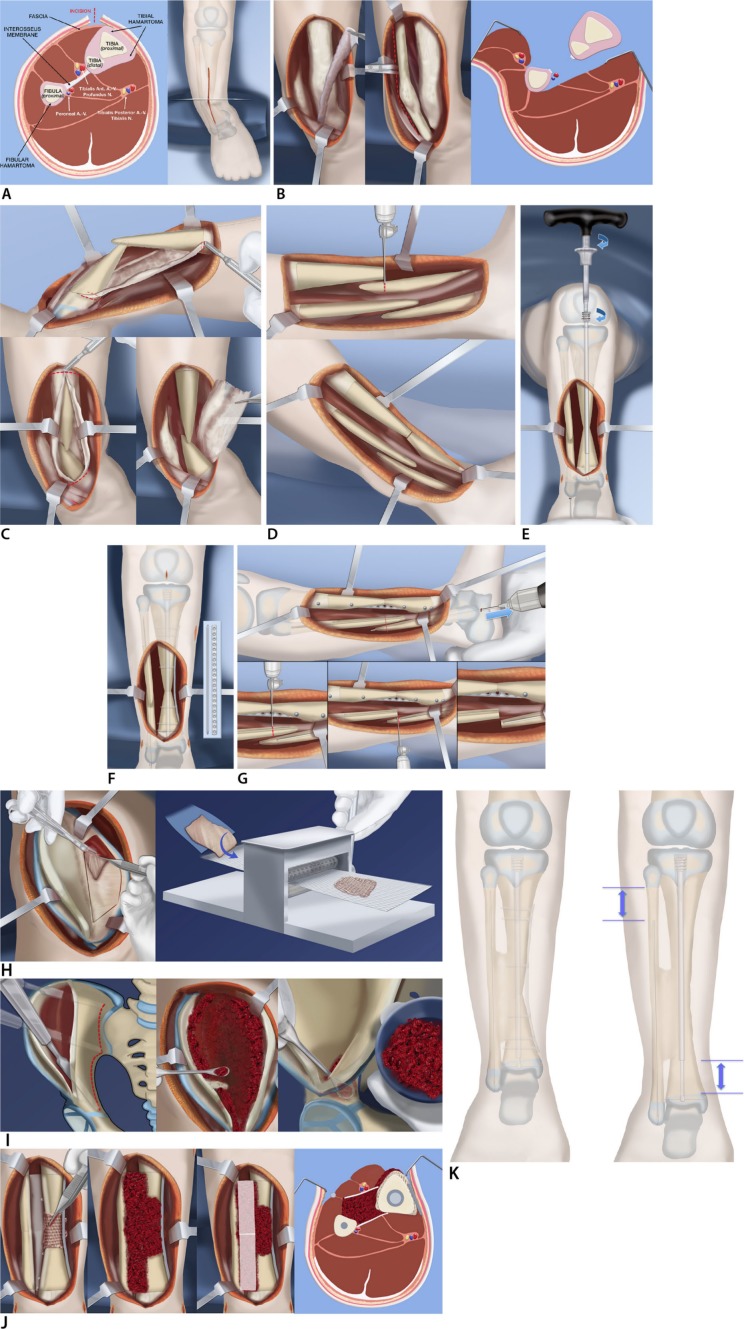
Fig. 2.
Reproduced with permission by the Paley Foundation: (a) anterior incision shown from front and cross section. Note hamartoma encircling tibia and fibula and the interosseous membrane between them; (b) anterior and deep posterior fasciotomy and muscle reflection to expose tibia, interosseous membrane, and fibula, allow resection of the membrane under direct vision without damage to the neurovascular bundles; (c) circumferential resection of the tibial fibrous hamartoma is carried out over the planned length of the cross-union. The same is done for the fibular hamartoma; (d) the tibial bowing is straightened and the bone ends overlapped and resected; (e) a customized Fassier-Duval telescopic nail is inserted and the male end locked with a wire into the distal epiphysis and the female end screwed into the proximal epiphysis; (f) a small diameter locking plate is fixed medially to the tibia with six screws; (g) the fibular ends can now be cut and the fibula fixed with a wire in its medullary canal; (h) a periosteal graft is harvested from the undersurface of the iliacus muscle. It is then expanded by passing it through the skin graft mesher; (i) decancellousization of the ilium is done by first splitting the two cortical tables of the ilium down to the roof of the acetabulum, triradiate cartilage, sciatic notch, posterior spines and sacro-iliac joint; (j) the periosteal graft is wrapped around the congenital pseudarthrosis site and bone morphogenic protein-2 (BMP2) collagen sponges are inserted overtop the posterior muscles behind the tibia and fibula (left). The cancellous bone is inserted between the tibia and fibula (left centre). The BMP2 sponges are placed overtop the bone graft (right centre). The anterior muscles lie over the BMP2. The interosseous space has a sandwich of cancellous bone between layers of BMP2 and its overlying soft tissues; (k) the cross-union forms between the bones by three months after surgery. The bone is well fixed with the telescopic rod in the tibia, the wire in the fibula and the plate on the tibia (left). Growth may occur despite the hardware leading to telescopic expansion of the male and female rods. The fibular wire descends with growth (left).