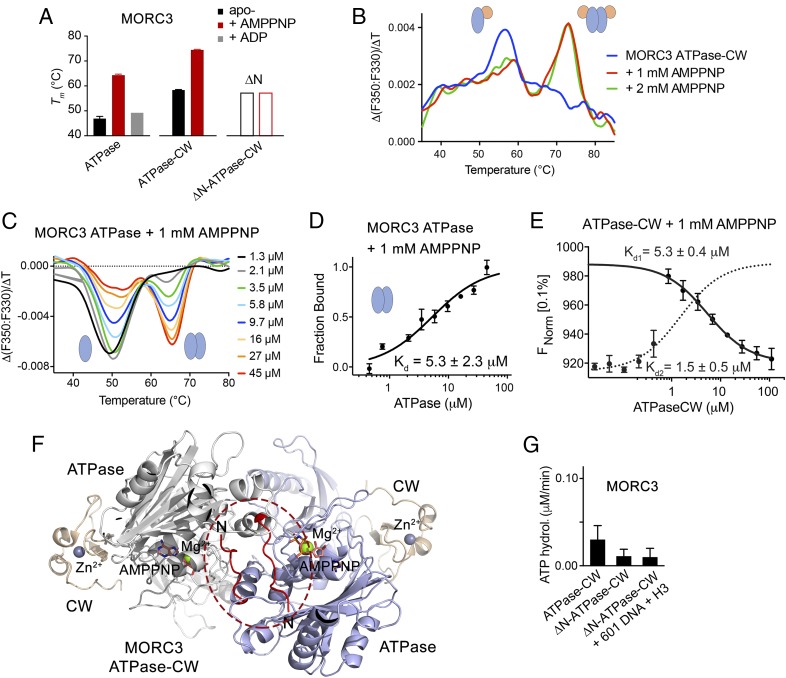
Fig. 3.
Dimerization of MORC3 is required for ATPase activity. (A) Tms derived from DSF for the ATPase domain, ATPase–CW cassette, and N-terminally truncated ATPase–CW of MORC3 in the absence (black) or presence (red) of 1 mM AMPPNP or ADP (gray). Error bars represent an SEM based on two separate experiments. (B and C) AMPPNP-induced MORC3 ATPase–CW (B) or ATPase (C) dimerization monitored by DSF. (D) MST binding curve used to determine Kd for the MORC3 ATPase dimerization. Error represents SD between three separate experiments; Kd values ± SD are shown. (E) MST binding curves used to determine Kds for the MORC3 ATPase–CW dimerization (solid line) and ATPase–CW/H3 interaction (dashed line). Error represents SD between three separate experiments; Kd values ± SD are shown. (F) Ribbon diagram of the ATPase–CW dimer as in Fig. 1E with the N terminus (residues 9 to 16) colored red and encircled by a red oval. (G) Rates of ATP hydrolysis by the MORC3 ATPase–CW cassette, WT and ∆N mutant. Error represents SD of at least three separate experiments.