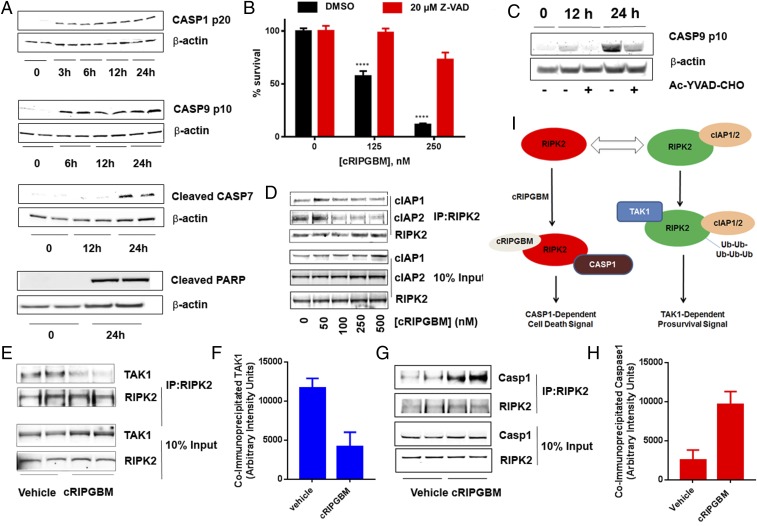
Fig. 3.
cRIPGBM activates caspase 1-mediated apoptotic signaling in GBM CSCs by modulating the interaction of RIPK2 with TAK1 and caspase 1. (A) Time-dependent cRIPGBM (250 nM)-induced cleavage of caspase 1, caspase 9, caspase 7, and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) in GBM-1 GBM CSCs. (B) cRIPGBM-induced cell death in GBM-1 GBM CSCs following treatment with the pan-caspase inhibitor Z-VAD (20 μM). (C) cRIPGBM-induced (250 nM) caspase 9 cleavage in GBM-1 GBM CSCs following treatment with the caspase 1-selective inhibitor Ac-YVAD-CHO (20 μM). (D) Coimmunoprecipitation of cIAP1 and cIAP2 with anti-RIPK2 antibody in GBM-1 GBM CSCs following treatment with cRIPGBM. (E) Coimmunoprecipitation of TAK1 with anti-RIPK2 antibody in GBM-1 GBM CSCs following treatment with cRIPGBM (250 nM). (F) Quantification of TAK1 levels coimmunoprecipitated by using an anti-RIPK2 antibody in GBM-1 GBM CSCs following treatment with cRIPGBM (250 nM). (G) Coimmunoprecipitation of caspase 1 with anti-RIPK2 antibody in GBM-1 GBM CSCs following treatment with cRIPGBM (250 nM). (H) Quantification of caspase 1 levels coimmunoprecipitated by using an anti-RIPK2 antibody in GBM-1 GBM CSCs following treatment with cRIPGBM (250 nM). (I) Schematic representation of the proposed mechanism of action for cRIPGBM-induced apoptosis in GBMB CSCs. Values shown are mean ± SD (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.005, and ****P < 0.001).