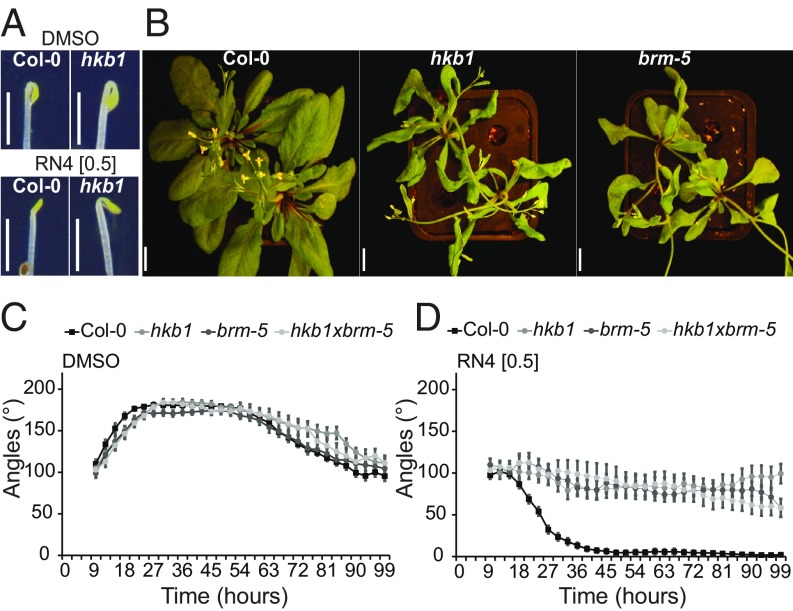
Fig. 6.
The hkb1 mutant is resistant to the RN4 effect on apical hook development and carries a mutation on BRM. (A) Comparison of apical hook phenotype in Col-0 and hkb1 seedlings 24 h after germination in the dark. The seedlings were grown on media supplemented with DMSO (Upper) or RN4 (Lower). (Scale bars, 2 mm.) (B) Four-week-old Col-0, hkb1, and brm-5 grown in long-day greenhouse conditions. (Scale bars, 1 cm.) (C and D) Apical hook angle in Col-0, hkb1, brm-5, and hkb1xbrm-5 grown on DMSO (C) and 0.5 µM RN4 (D) supplemented media for 6 d in the dark. Measurement of apical hook angle was performed every 3 h. Means ± SEM are shown, n > 18 seedlings across two independent replicates. Concentrations in micromolars are indicated in brackets.