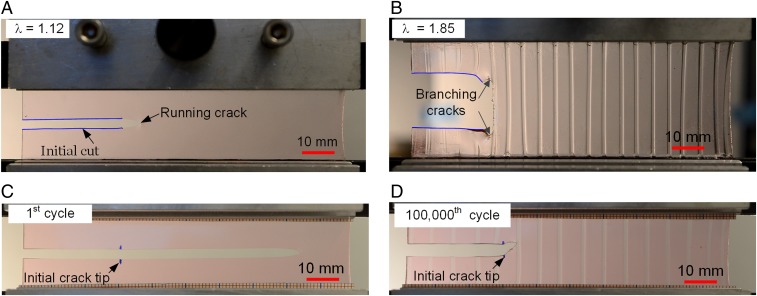
Fig. 2.
Fracture and fatigue of homogeneous PDMS and composite PDMS. Each sample is glued to two rigid clamps, and precut with a crack using a razor blade. (A) A homogeneous hard PDMS ruptures at a monotonic stretch of 1.12. (B) A composite PDMS does not rupture at a monotonic stretch of 1.85. (C) When a homogeneous hard PDMS is subjected to cycles of load and unload of maximum stretch of 1.2, the crack extends rapidly before reaching the maximum stretch in the first cycle. (D) When a composite PDMS is subjected to cycles of load and unload of maximum stretch of 1.2, the crack extends to the first fiber in front within 1,000 cycles, but then arrests without any further extension over 100,000 cycles. A:B = 10:1 for the homogeneous hard PDMS. For the composite, A:B = 10:1 for the fibers, and 30:1 for the matrix.