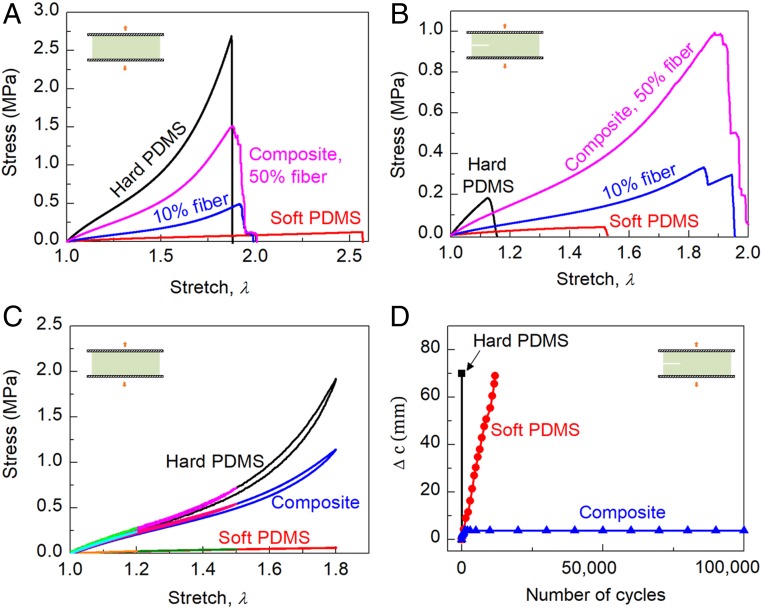
Fig. 3.
Flaw insensitivity, low hysteresis, and fatigue resistance. (A) Stress–stretch curves of samples without precut cracks stretched monotonically to rupture. The stress is defined as the force applied on the deformed sample divided by the cross-sectional area of the undeformed sample. (B) Stress–stretch curves of samples with precut cracks stretched monotonically to rupture. (C) Stress–stretch curves of samples without precut cracks subjected to loading and unloading to measure hysteresis. (D) Samples with precut cracks are cycled between stretches 1 and 1.2. The extension of the crack, , is recorded as a function of the number of cycles. A:B = 10:1 for the hard PDMS and for the fibers of composite PDMS. A:B = 30:1 for the soft PDMS and the matrix of the composite PDMS.