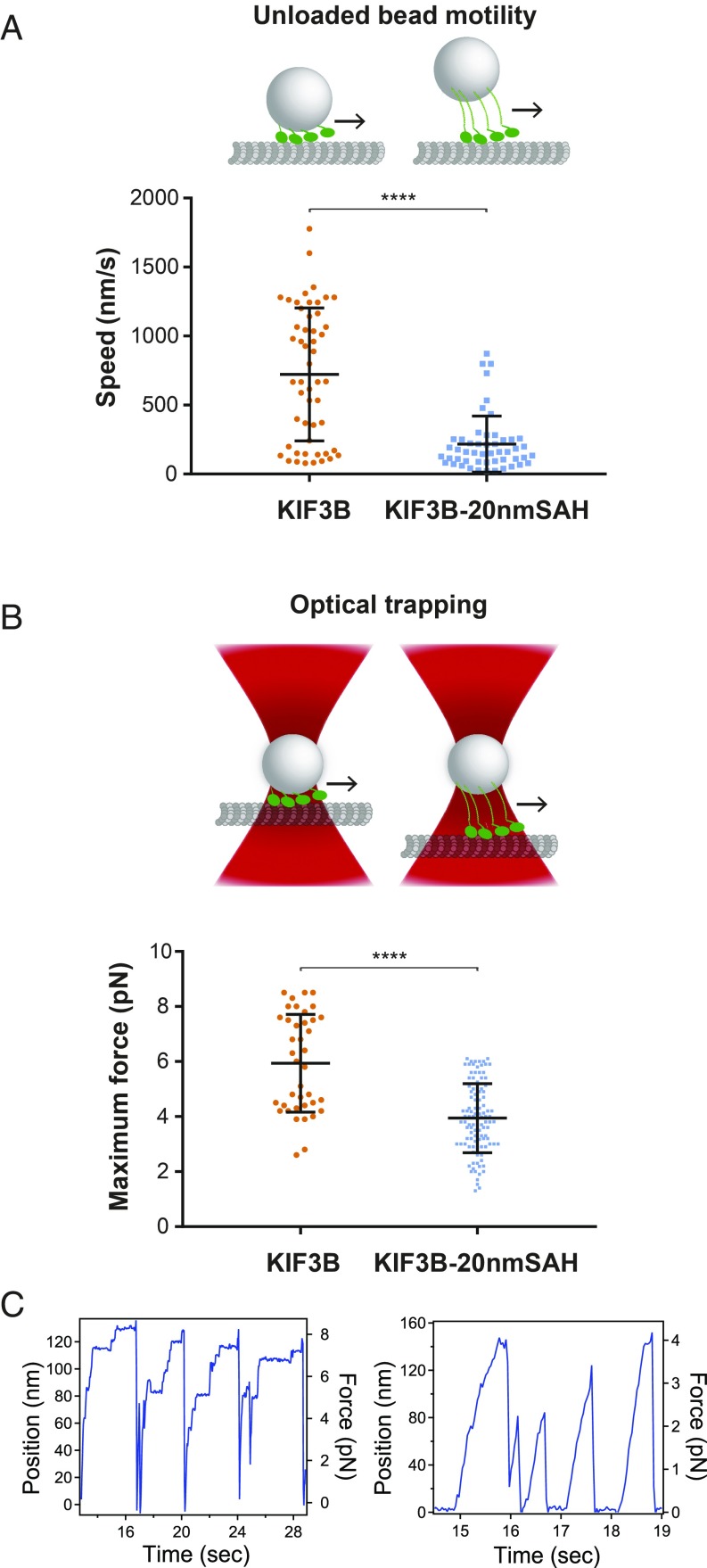
Fig. 7.
A short motor-to-cargo linker enables KIF3B monomers to drive faster unloaded bead motility and generate higher forces. Monomeric KIF3B(1-350) motors containing no extension (KIF3B) or a 20-nm SAH extension (KIF3B-20nmSAH) were biotinylated, bound to 0.4-μm streptavidin beads, and tested for their ability to drive transport and generate force. (A, Upper) Schematic of unloaded bead motility assays. Fluorescent beads with bound biotinylated motors were imaged by TIRF microscopy and their speeds were measured by kymograph. (Lower) KIF3B monomers: average bead motility 723 ± 482 nm/s (SD), n = 52 events over three independent experiments; KIF3B-20nmSAH monomers, average bead motility 217 ± 204 nm/s (SD), n = 51 over three independent experiments. ****P < 0.0001 (two-sample Kolmogorov–Smirnov test). (B, Upper) Schematic of optical trapping assay. (Lower) KIF3B monomers average stall forces 5.9 ± 1.8 pN (SD), n = 39 events over three independent experiments; KIF3B-20nmSAH monomers 3.9 ± 1.3 pN (SD), n = 108 events over three independent experiments. ****P < 0.0001 (two-sample Kolmogorov–Smirnov test). (C) Example traces of optically trapped beads coated with KIF3B monomers (Left) or KIF3B-20nmSAH monomers (Right).