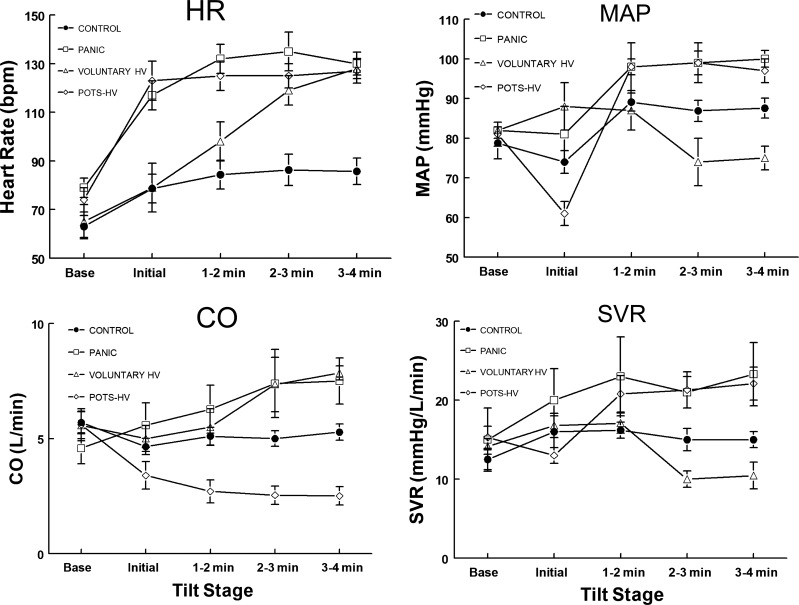
Fig. 3.
Heart rate (HR), mean arterial pressure (MAP), cardiac output (CO), and systemic vascular resistance (SVR) from Voluntary HV, POTS-HV, Panic, and Control subjects. HR increased significantly (P < 0.001) during periods of hyperventilation for all groups. MAP increased in POTS-HV and Panic, whereas Voluntary HV was significantly reduced compared with all other groups (P < 0.025). CO decreased significantly (P < 0.005) in POTS-HV, in Panic (P < 0.025), and in Panic and Voluntary HV. SVR increased significantly in POTS-HV (P < 0.005) and Panic (P < 0.025) but decreased significantly (P < 0.01) in Voluntary HV. HV, hyperventilation; Panic, panic disorder; POTS, postural tachycardia syndrome.