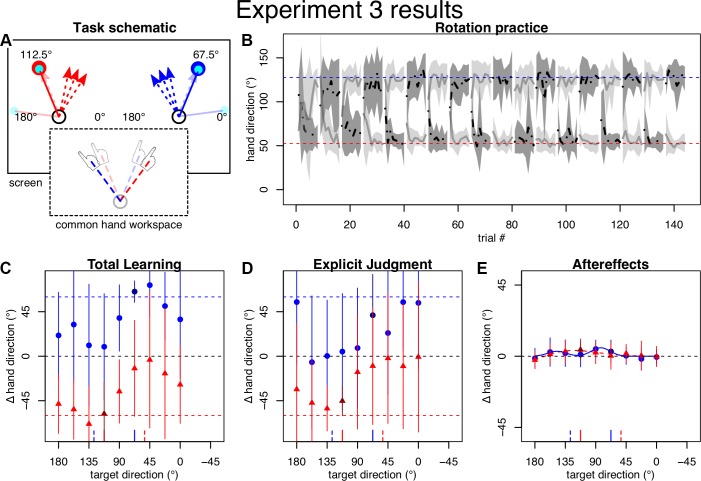
Fig. 4.
Task and results of experiment 3. A: visual target directions were separated by 45° and the cursor rotated outward so that strategies should cross the midline and point approximately at the other target. The multiple dashed arrows emphasize strategies changing over the course of learning (compared with experiment 4). B: practice performance was more variable compared with experiment 1 (A). C and D: total learning and explicit judgments flipped signs in line with the reversed cursor rotations cued by the separate visual workspaces. They also appeared more variable but resembled experiment 1 when 5 outliers were removed (not shown). E: aftereffects appeared dominated by interference, which did not change without the 5 outliers (not shown). Note that the lines indicating full compensation are outside the y-axis limits.