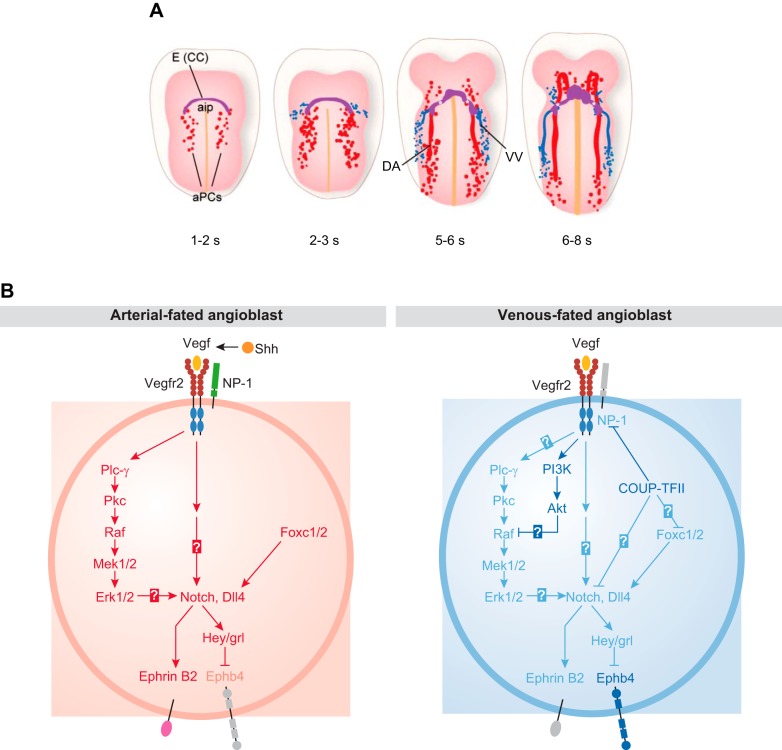
FIGURE 10.
First stages of embryonic vascular development in mice and the role of Notch signaling in arterial cell fate determination. A: at embryonic day 7.5 (E7.5) (1−2 somite stage), the first angioblasts coalesce on both sides of the embryonic midline, posterior to endocardial precursor cells [cardiac crescent (CC), purple; anterior intestinal portal (aip)]. In the following stages of embryonic development, these arterial precursor cells (aPCs), formed through vasculogenesis, give rise to the paired dorsal aortas (DA). By the 2–3 somite stage (~E8.5), the first venous precursors appear adjacent to the aPCs and eventually coalesce to form the vitelline vein (VV), and ultimately give rise to the cardinal veins. B: sonic hedgehog (Shh) produced by the notochord and floorplate promotes production of high levels of VEGF in the somites, which activates angioblasts from the lateral plate mesoderm. Left: VEGF, in turn, activates the VEGFR2 and neuropilin 1 expressed on the surface of aPCs. This particular configuration of high VEGF coupled with VEGFR2/neuropilin 1 signaling in aPCs activates a signaling cascade, including phospholipase Cγ-1 (Plc-γ) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (Erk) that ultimately stimulates production of Notch and Delta-like 4 (Dll4) in aPCs. Dll4-activated Notch signaling upregulates the arterial marker ephrinB2 while suppressing the venous marker EphB4. Right: in the presence of low levels of VEGF, venous fated angioblasts express the venous marker chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor II (COUP-TFII), which suppresses the expression of neuropilin 1, a membrane-bound co-receptor for VEGF that is required to induce an arterial phenotype, and the downstream expression of Notch. This altered signaling pathway results in preferential expression of the vein marker EphB4. Please note that both Notch and Dll4 are membrane-anchored proteins present on the cell surface and are only indicated inside the cell to illustrate the control of their gene expression by key upstream regulators. Ephb4, B4 ephrin receptor; grl, gridlock; Hey, hairy-and-enhancer-of-split related; Mek, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; Pkc, protein kinase c. [We thank Kate Wythe for preparing the illustrations in A, which were adapted from Fish and Wythe (72), with permission from Dev Dyn; B was adapted from Lin et al. (153), with permission from EMBO Rep.]