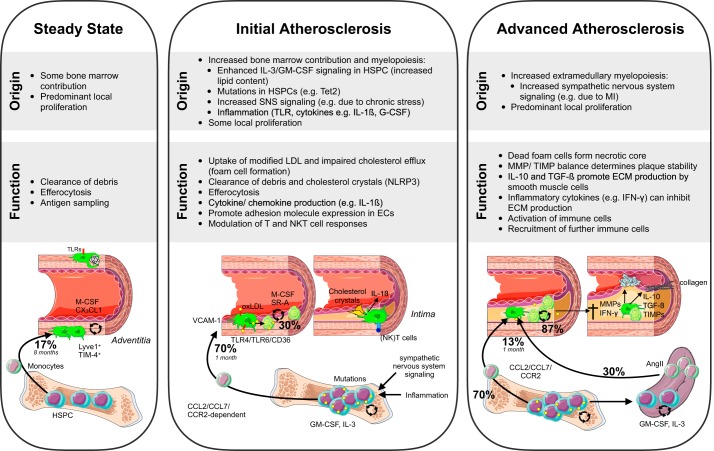
FIGURE 3.
Macrophage origin and function in steady-state and diseased vessels. Aortic macrophage ontogeny and role during steady-state and atherosclerosis initiation and progression are illustrated for each stage. For simplicity, only the role of macrophages is depicted. The role of other immune cells, endothelial cells, and vascular smooth muscle cells is not shown. Percentages indicate contribution of monocyte recruitment or local proliferation to macrophage origin over the indicated amount of months. AngII, angiotensin II; ECs, endothelial cells; ECM, extracellular matrix; GM-CSF, granulocyte macrophage-CSF; HSPCs, hematopoietic stem and progenitors cells; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; M-CSF, macrophage-colony-stimulating factor; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; MI, myocardial infarction; MMPs, matrix metalloproteinases; NK, natural killer; NLRP, NACHT, LRR, and PYD, domains containing protein; oxLDL, oxidized LDL; SR-A, scavenger receptor A; Tet2, Tet methylcytosine dioxygenase 2; TGF, transforming growth factor; TIMPs, tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases; TLRs, Toll-like receptors.