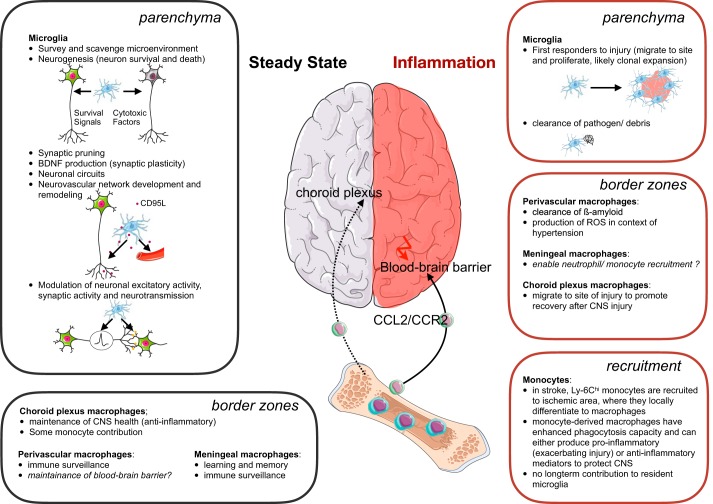
FIGURE 5.
Macrophage origin and function in the steady-state and injured brain. Microglia and border zone macrophage functions are illustrated in steady state and inflammation. Monocytes do not contribute to most central nervous system (CNS) macrophages in the steady state, with the exception of choroid plexus macrophages. After injury or stroke, the blood-brain barrier is disrupted, and monocytes can be recruited in large numbers and transiently give rise to macrophages. BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; ROS, reactive oxygen species.