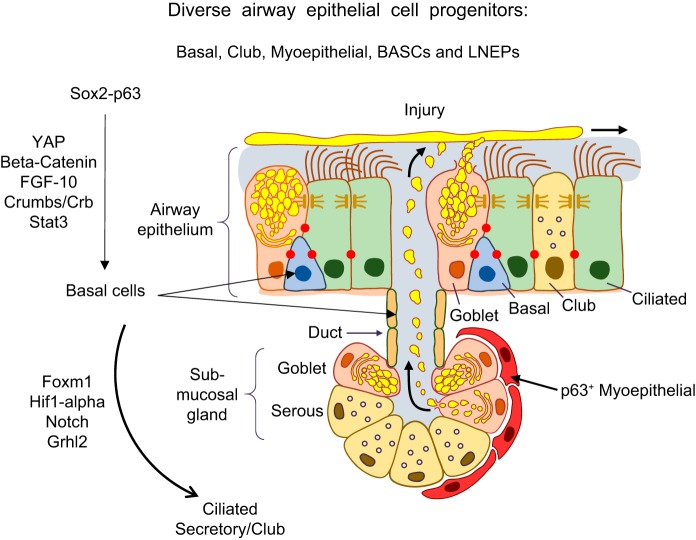
FIGURE 12.
Diverse progenitor cells repair the conducting airway epithelium. The conducting airway surface and submucosal glands are shown. Basal cells (SOX2, TP63) are the primary progenitor-stem cells in the pseudostratified regions of the conducting airways. Basal cells in the ducts of submucosal glands and myoepithelial cells in the submucosal glands also serve as progenitors from which ciliated, basal, and secretory cells are produced. Secretory (club) cells also serve as proliferative progenitors following injury. Signaling and transcriptional networks regulating cell migration, proliferation, and redifferentiation following lung injury are shown. Bronchoalveolar stem cells (BASCs) and lineage negative epithelial progenitors (LNEPs) represent additional progenitor cells types (not shown).