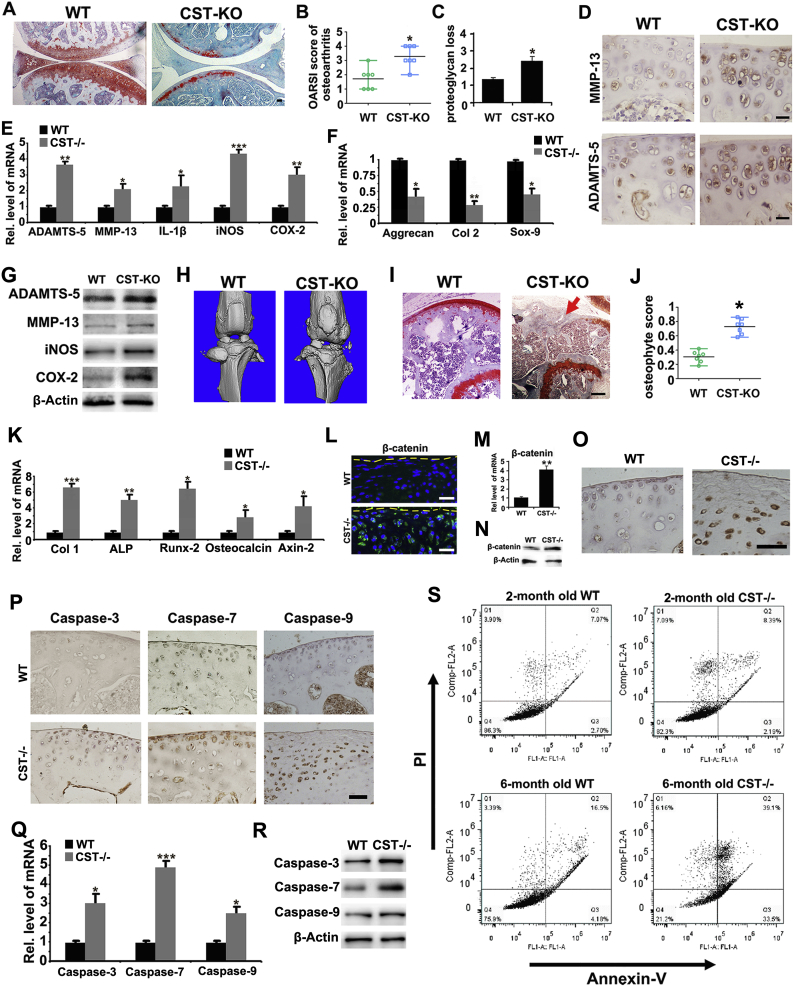
Fig. 3.
Deficiency of CST exaggerates the development of spontaneously developed OA. (A) Deficiency of CST caused more loss of proteoglycan in articular cartilage in 10-month-old CST−/− mice than in WT mice as detected by safranin O staining compared. (B, C) A lack of CST exacerbates OARSI scores and OA phenotypes in aging mice. (D) Expression of MMP-13 and ADAMTS-5 greatly increase in CST−/− mice as detected by immunohistochemistry. (E) ADAMTS-5, MMP-13, IL-1β, iNOS and COX-2 were elevated in CST−/− mice as detected by Real-time PCR. (F) Aggrecan, Col-2 and Sox-9 were diminished in CST−/− mice as detected by Real-time PCR. (H) Osteophyte formation and ectopic subchondral sclerosis were detected through micro-CT scanning. (I-J) Safranin O staining and osteophyte score of the knee joint on the basis of histology were examined to detect osteophyte formation (red arrow) and ectopic subchondral sclerosis. (K) Col-1, ALP, Runx-2, osteocalcin and Axin-2 were elevated in CST−/− mice, as detected by Real-time PCR. (L) β-Catenin was elevated in CST−/− mice, as detected by immunofluorescence. (M) β-Catenin was increased in CST−/− mice, as detected by Real-time PCR. (N) β-Catenin was upregulated in CST−/− mice, as detected by western blotting. (O) Expression of β-catenin showed a considerable increase in CST−/− mice, as detected by immunohistochemistry. (P) Expression of caspase-3, caspase-7 and caspase-9 was enhanced in CST−/− mice, as detected by immunohistochemistry. (Q) Caspase-3, caspase-7 and caspase-9 levels increased in CST−/− mice, as detected by Real-time PCR. (P) Secretion of caspase-3, caspase-7 and caspase-9 was upregulated in CST−/− mice by western blotting. (R) CST−/− mice showed substantial apoptosis that increased over time, as detected by flow cytometry. (S) Detection of apoptosis of primary mouse chondrocytes of 2/6-month-old WT/CST−/− mice. (*p < .05, **p < .01, ***p < .005 vs control group). n = 7 for each group, Scale bar: 100 μm. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)