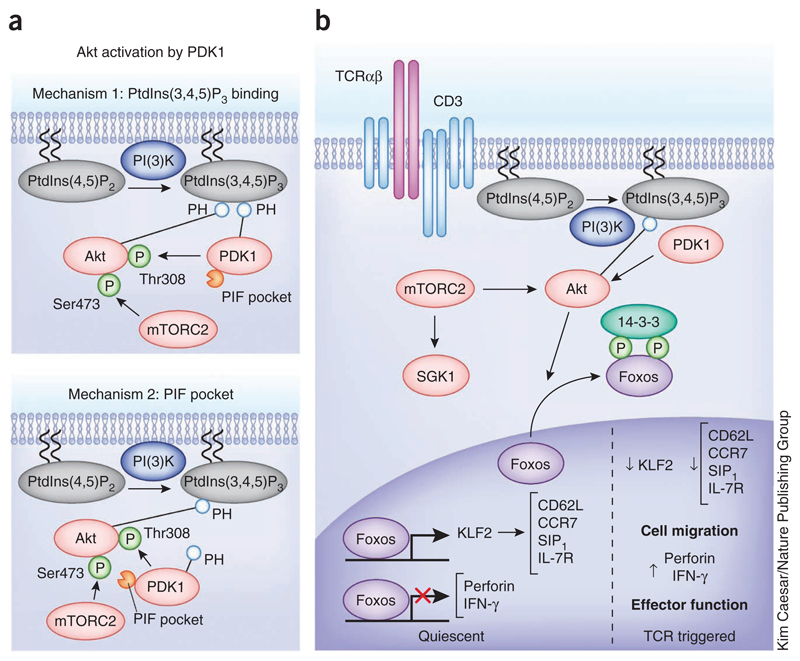
Figure 3.
The PtdIns(3,4,5)P3-regulated serine-threonine kinase Akt. (a) Mechanisms of Akt activation by PDK1. Two described mechanisms for colocalization of Akt and PDK1; one is dependent on PDK1 binding to PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 and the other is dependent on PDK1 recruitment to Akt via mTORC2-mediated Ser473 phosphorylation. (b) Role of Akt in TCR signal transduction. Akt activation by PDK1 has a key role in T cell activation, regulating the subcellular localization and function of the Foxo family of transcription factors. Foxos regulate the expression of key molecules that control T cell trafficking and effector functions.