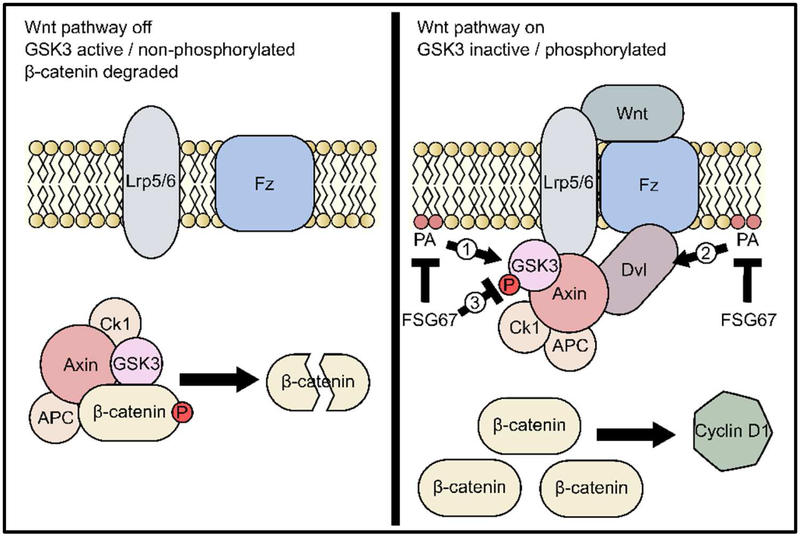
Figure 7. Mechanisms by which FSG67 may affect Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
When Wnt/β-catenin signaling is off, the β-catenin destruction complex composed of GSK3β, APC, CK1 and Axin targets β-catenin for destruction. When Wnt binds to Frizzled (Fz) and the Lrp co-receptors, the destruction complex is held inactive at the plasma membrane and β-catenin accumulates and upregulates transcription of pro-proliferation genes like cyclin D1. FSG67 may act by inhibiting synthesis of phosphatidic acid (PA) and lysoPA, which may normally inhibit GSK3β either directly (1) or through an effect mediated by disheveled (Dvl) (2). Alternatively, FSG67 may itself have an effect on GSK3β (3).