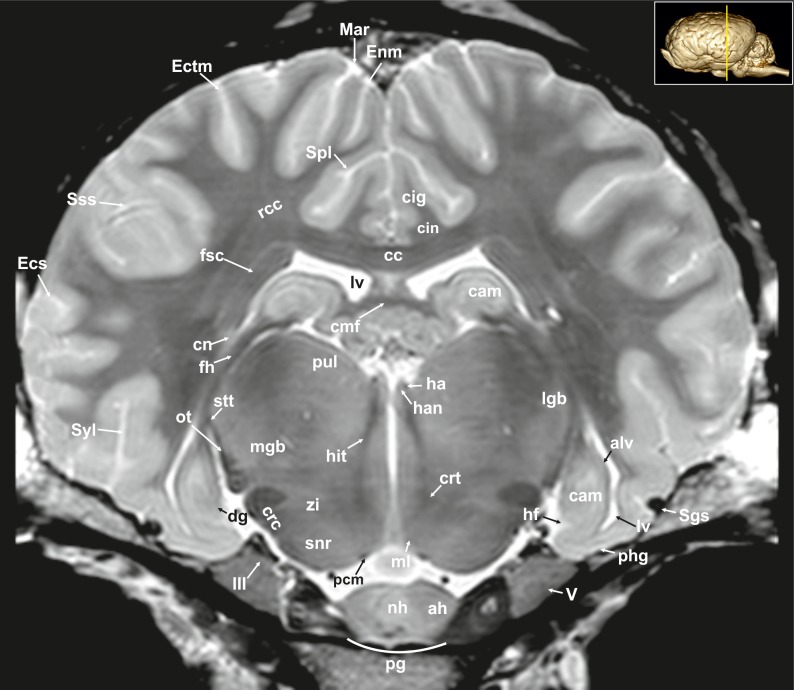
Fig 8. Transverse magnetic resonance image of the equine on the level of the hippocampus.
ah: adenohypophysis, alv: alveus, cam: ammon’s horn, cc: corpus callosum, cin: cingulum, cmf: commissure of fornix, cn: caudate nucleus, crc: cerebral crus, crt: rubro-cerebello-thalamic tract, dg: dentate gyrus, Ecs: ectosylvian sulcus, Ectm: ectomarginal sulcus, Enm: endomarginal sulcus, fh: fimbria of the hippocampus, fsc: subcallosal fasciculus, ha: habenula, han: habenular nuclei, hf: hippocampal fissure, hit: habenulo-interpeduncular tract, lgb: lateral geniculate body, lv: lateral ventricle, Mar: marginal sulcus, max: maxillary nerve, mgb: medial geniculate body, ml: medial lemniscus, nh: neurohypophysis, ot: optic tract, pcm: peduncles of the mammillary body, phg: parahippocampal gyrus, pul: pulvinar nuclei, rcc: radiation of corpus callosum, Sgs: sagittal sulcus, snr: substantia nigra, Sss: suprasylvian sulcus, stt: terminal stria; Syl: sylvian fissure, zi: zona incerta, III: oculomotor nerve.